Mastering the Purchasing Process: Everything You Need to Know
Procurement and digital transformation are synonymous in today’s competitive business landscape.
Whether sourcing materials for manufacturing, negotiating supplier contracts, or tracking expenses, companies are increasingly relying on automation and data-driven technologies to streamline purchasing workflows. These advancements reduce error-prone manual data entry and foster better supplier relationships and optimize the entire procurement cycle.
A well-oiled purchasing process ensures that organizations acquire the necessary goods and services efficiently, cost-effectively, and with minimal risk.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential steps of the purchasing process and explore how modern businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make smarter purchasing decisions.
Purchasing vs procurement: What’s the difference?
The purchasing process refers to the series of steps businesses take to acquire the goods and services they need for day-to-day operations. It is a subset of the broader procurement process, which encompasses not only purchasing but also vendor selection, contract negotiations, and strategic sourcing.
The purchasing process, on the other hand, focuses on the operational aspects of procurement—creating purchase orders (POs), tracking supplier performance, and ensuring goods and services meet quality standards.
While procurement is more strategic, involving long-term planning and vendor management, purchasing is more transactional, dealing with the mechanics of acquiring goods. Both processes are essential to ensuring businesses can meet their operational needs without overspending or compromising on quality. Learn more about procurement vs purchasing.
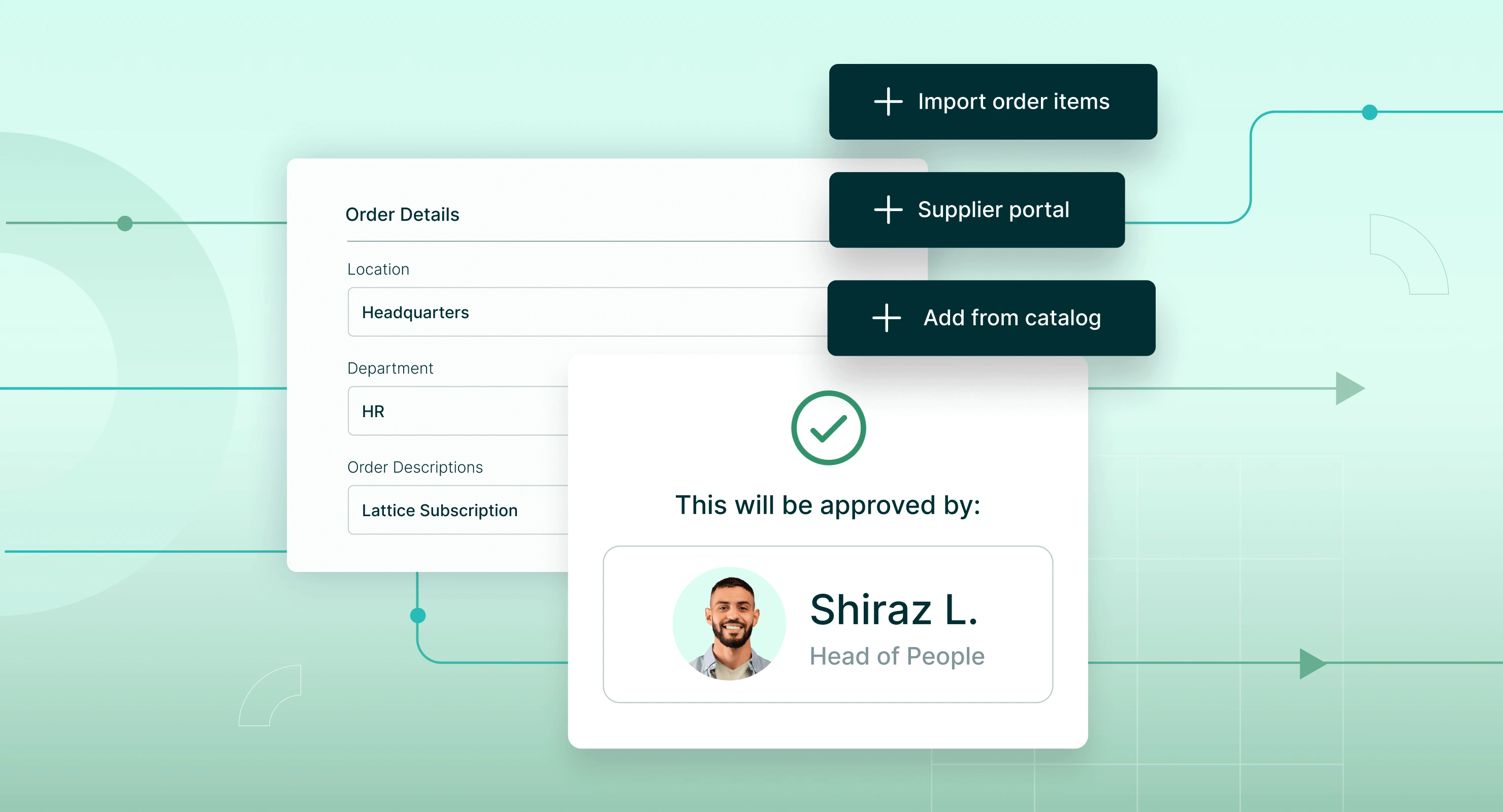
Ready to Automate Your Purchasing Process?
Procurify’s procure-to-pay software automates your company’s purchasing workflow from order creation and approvals to invoice payment – to speed up purchasing, improve internal communication, and minimize financial risk.
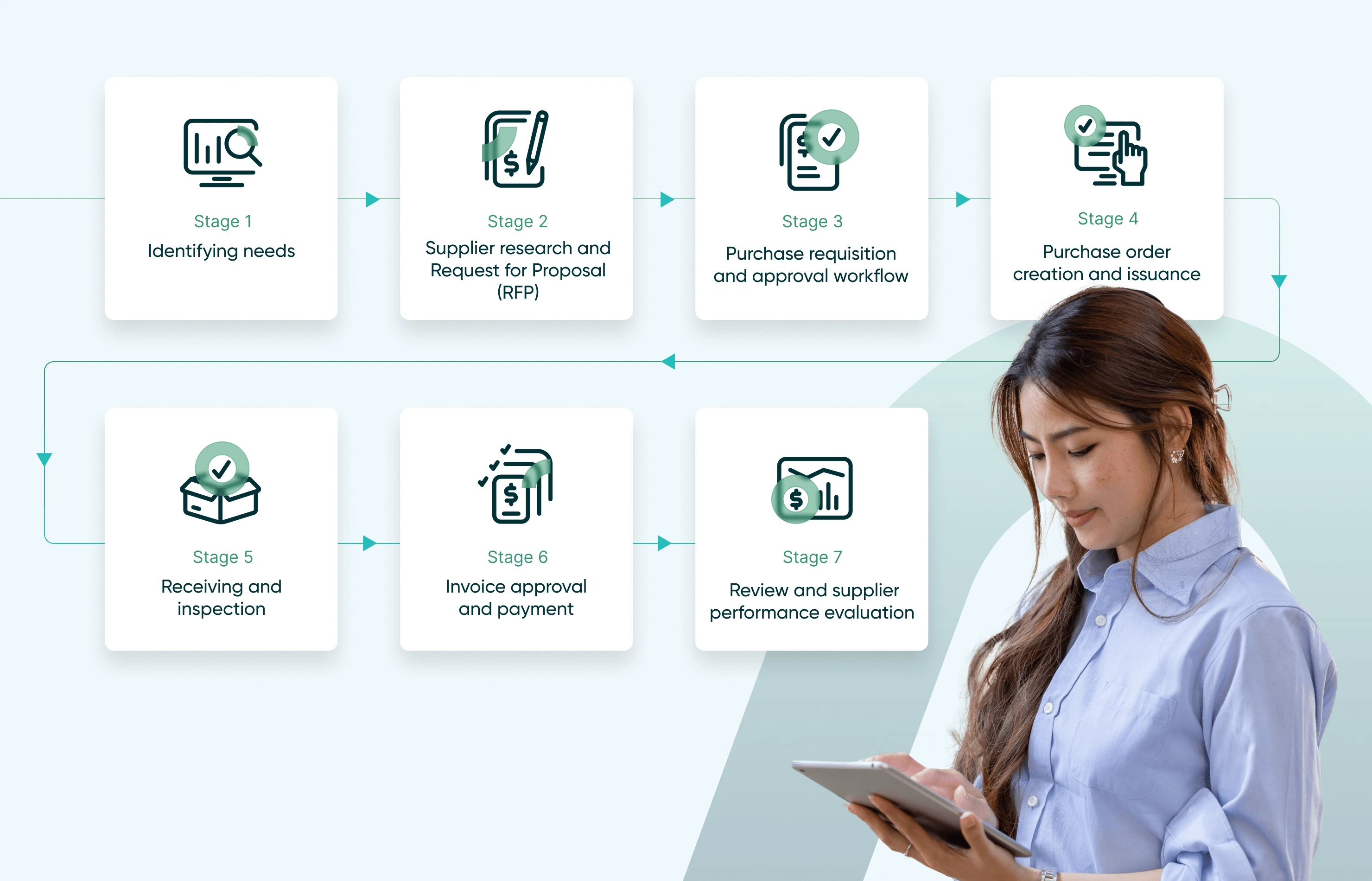
Key Stages of the purchasing process
-
Identifying needs
The first step in the purchasing process is understanding what your business needs. This involves various departments collaborating to identify the goods or services required to support daily operations. Whether it’s raw materials for manufacturing, new software for IT, or office supplies, accurately identifying these needs ensures that your purchasing efforts align with the company’s strategic goals.
In larger organizations, procurement teams rely on automation tools to track supply requests and forecast future needs. These tools can analyze historical data, helping businesses identify patterns in consumption and predict future demand. For example, a company that regularly orders packaging materials can use such tools to anticipate when reordering will be necessary, ensuring stock levels are always optimal.
By conducting regular reviews of departmental needs and benchmarking suppliers, companies can avoid over-purchasing and prevent supply shortages, both of which contribute to cost savings.
-
Supplier research and request for proposal (RFP)
After determining the specific business needs, the next step involves sourcing potential suppliers. This step is crucial for finding vendors who can meet your quality, budget, and timeline requirements. Companies typically send out Request for Proposals (RFP) to vendors. These documents outline the specific goods or services the business needs and invite suppliers to submit bids, detailing their ability to fulfill those requirements.
Effective supplier research involves more than just finding the lowest price. Strategic sourcing considers the supplier’s ability to deliver consistently, their reputation in the market, and their long-term reliability. Evaluating factors like lead time, production capacity, and financial stability ensures that you’re building partnerships with suppliers who align with your business goals. Advanced organizations often use e-procurement systems to streamline this process, automating the RFP distribution and bid evaluation.
Automation tools also enable businesses to maintain a list of pre-approved suppliers, which can shorten the procurement cycle by allowing companies to bypass the RFP stage for repeat purchases. Pre-vetted suppliers who have demonstrated consistent performance can be quickly mobilized to meet urgent needs, speeding up the overall process.
-
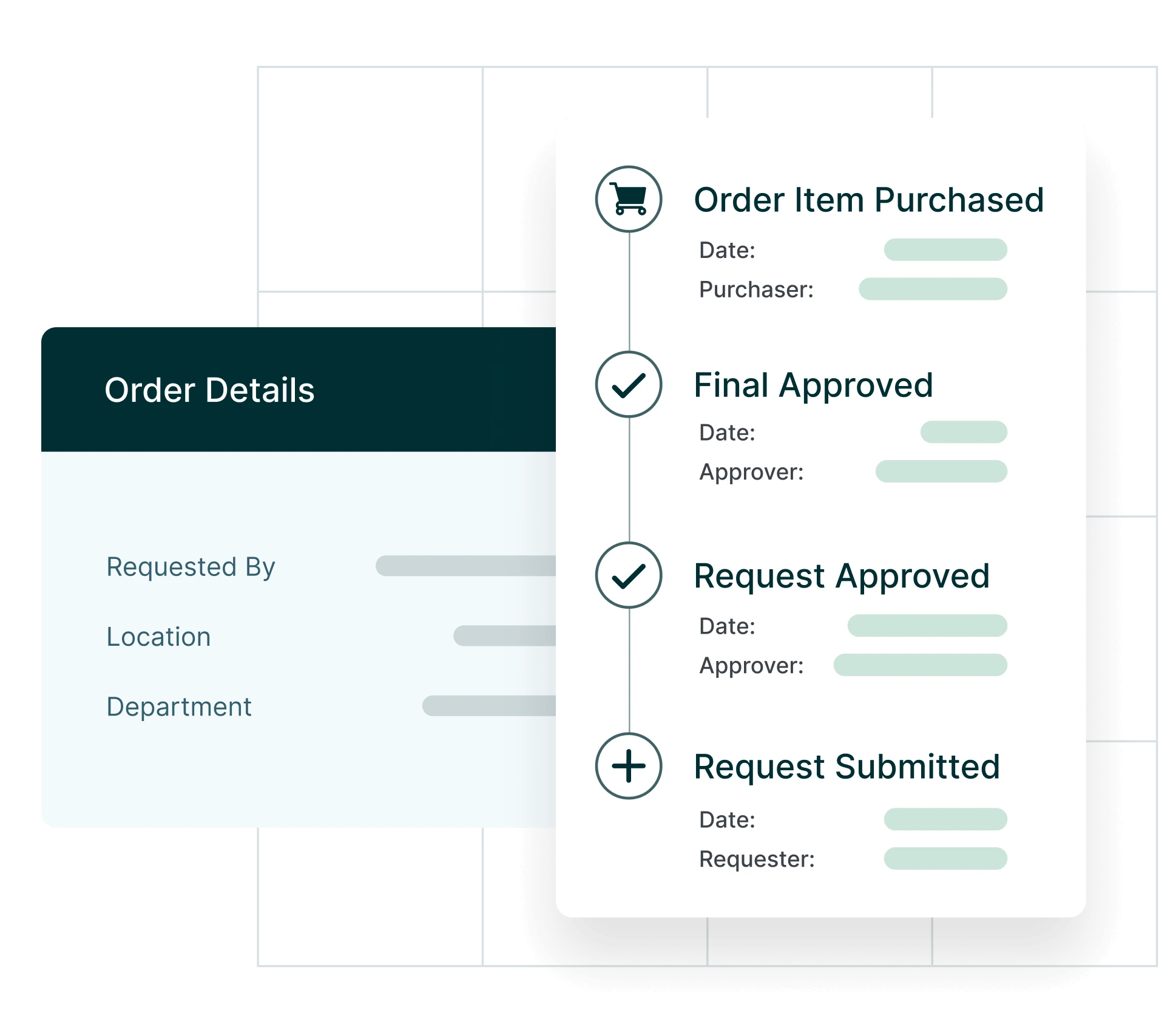
Purchase requisition and approval workflow
Once a vendor has been selected, the next step is to create a purchase requisition, a formal request to procure the goods or services. In many organizations, purchase requisitions require approval from department heads or finance managers to ensure that the requested purchases align with the budget.
In modern procurement systems, approval workflows are often automated, ensuring that all requests go through the necessary checks and balances without causing delays. For example, if a request exceeds a certain budget threshold, the system automatically routes the requisition to higher management for review. Conversely, low-cost, routine purchases may be pre-approved, reducing time spent on manual approvals.
This stage is essential for maintaining financial control over business expenses and preventing unauthorized purchases. By having a clear workflow in place, companies can avoid “rogue spend” (purchases made outside of approved budgets) and ensure that spending is consistently tracked.
-
Purchase order creation and issuance
Once the purchase requisition has been approved, it is converted into a purchase order (PO). A purchase order is a legally binding document that confirms the details of the transaction, including the quantity of goods, price, payment terms, and delivery schedule.
With modern e-procurement platforms, the creation and issuance of purchase orders can be automated, eliminating manual data entry errors and speeding up the process. When the PO is ready, it is sent to the supplier, who confirms receipt and begins preparing the goods or services for delivery.
In some cases, companies may skip this step for small, routine purchases, but larger or more complex transactions need to have clear documentation for legal and auditing purposes.
-
Receiving and inspection
Once the goods or services are delivered, it’s critical to inspect them to ensure they match the specifications outlined in the purchase order. This step helps businesses verify that the correct quantity, quality, and type of goods have been delivered.
Organizations often implement quality control measures such as visual inspections or functional tests to detect any discrepancies early on. These measures are essential, especially for high-value goods or components that could impact production or service delivery.
Proper documentation is also maintained at this stage, including delivery receipts and inspection reports, which are vital for supporting payment processing and maintaining an audit trail.
Issues with goods or services may arise, such as damaged products or incorrect quantities. Having an efficient returns or dispute resolution process in place ensures that these problems are addressed swiftly, preventing disruptions in operations.
-
Invoice approval and payment
After receiving and inspecting the goods, the supplier will issue an invoice. This stage requires careful attention to ensure the invoice matches the terms set out in the purchase order and the actual delivery. Companies employ a process called three-way matching to compare the purchase order, delivery receipt, and invoice. If all three documents align, the invoice is approved for payment.
Automating the invoice approval process through Accounts Payable (AP) automation tools can significantly reduce processing time and human errors.
These tools automatically match invoices with corresponding purchase orders and delivery receipts, flagging discrepancies for review. This automation allows businesses to pay their suppliers promptly, maintaining good relationships and often benefiting from early payment discounts.Timely payment is not just beneficial for maintaining a strong supplier relationship; it also helps in managing the company’s cash flow efficiently. Delayed payments can incur penalties, which can hurt both the company’s finances and its rapport with suppliers.
-
Review and supplier performance evaluation
Once the purchasing process is complete and payment has been made, it’s time to evaluate the performance of the supplier. This step is often overlooked but is critical to ensuring that the supplier meets the long-term needs of the business. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as on-time delivery rates, product quality, and compliance with terms should be tracked regularly.
Supplier performance evaluations help businesses decide whether to continue working with a vendor, negotiate better terms, or even switch suppliers if performance is lacking. For strategic sourcing decisions, this evaluation is crucial in building a reliable supply chain that minimizes risk.
By collecting data on suppliers over time, businesses can also benchmark performance, allowing them to identify top-performing vendors and those that need improvement. This process also supports a more data-driven procurement strategy, where decisions are based on past performance rather than assumptions.
Challenges in the purchasing process
While the purchasing process is designed to ensure efficiency, several challenges can arise, particularly in manual or outdated systems. Common challenges include:
-
Human error: Manual processes are prone to mistakes, especially when dealing with large volumes of transactions. Misplacing or inaccurately processing an invoice can lead to delayed payments or incorrect orders.
-
Approval delays: When approvals rely on manual systems or disjointed communication, delays are inevitable. For example, if an approver is unavailable, the entire process may stall, causing downstream impacts on operations.
-
Siloed teams: In organizations where procurement, finance, and operations teams are not well integrated, it’s easy for miscommunication to occur. This lack of visibility can lead to double ordering or missed opportunities to negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Best practices for optimizing the purchasing process

Optimizing the purchasing process is crucial for businesses looking to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and build stronger relationships with suppliers. Here are some best practices to consider:
Embrace automation
Manual, paper-based purchasing workflows can create bottlenecks and increase the likelihood of errors. One of the most transformative actions a business can take is to automate key steps in the purchasing process. Automated workflows for tasks like purchase requisitions, approvals, and invoice matching help speed up processes and reduce human errors.
By implementing procurement software, companies can ensure real-time visibility into spending, supplier performance, and order statuses, which streamlines decision-making. Tools like AP automation and e-procurement platforms also enable faster invoice processing, ensuring that businesses can capture early payment discounts and maintain strong supplier relationships.
Standardize processes
Standardization is key to ensuring consistency and compliance in purchasing activities. By creating uniform procedures for requisition submission, approval workflows, and purchase orders, businesses can reduce confusion among employees and ensure that everyone follows the same steps.
Standardized processes also make it easier for management to monitor performance and ensure that procurement policies are being followed. For example, setting up clear thresholds for when approvals are needed or creating templates for purchase orders ensures that tasks are completed accurately and on time.
Strengthen supplier relationships
Building strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers goes beyond getting the best price. Supplier relationship management (SRM) focuses on long-term partnerships that offer mutual benefits.
Regular performance evaluations, clear communication, and shared goals help businesses get the most value from their suppliers.
Strong supplier relationships can result in better terms, priority service, and access to innovative products. Businesses that cultivate these partnerships often find that suppliers are more willing to negotiate on pricing, offer faster delivery, and assist in resolving any challenges that arise.
Use data and analytics
In the age of digital transformation, data is a powerful tool for optimizing procurement. By tracking metrics like spending patterns, supplier performance, and purchasing cycle times, companies can gain valuable insights into where they can cut costs or improve processes.
Procurement teams that leverage data analytics can make better-informed decisions, such as identifying underperforming suppliers or recognizing opportunities to consolidate purchases to negotiate bulk discounts.
Over time, this data-driven approach supports continuous improvement across all purchasing activities.
KPIs to measure purchasing effectiveness
To ensure the purchasing process operates efficiently and aligns with business goals, it’s essential to track key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics provide valuable insights into areas of success and those that need improvement. Some important KPIs to monitor include:
-
Procurement cycle time: This KPI measures the time taken from the identification of a need to the delivery of goods or services. A shorter cycle time indicates a more efficient process. Organizations that automate purchase requisitions and approvals often see significant reductions in cycle times.
-
Cost savings: This metric tracks the reductions in costs achieved through effective procurement activities, including negotiated discounts, bulk purchasing, or the elimination of unnecessary purchases. Businesses that use data-driven procurement strategies often find hidden cost-saving opportunities by analyzing spending patterns.
-
On-time delivery rate: Monitoring how often suppliers deliver goods on or before the agreed-upon date helps assess the reliability of your vendors. A high on-time delivery rate contributes to smoother operations and fewer production delays.
-
Spend under management: This KPI measures the percentage of an organization’s total spend that is actively managed by the procurement team. A higher percentage suggests better control and optimization of purchasing activities.
-
Supplier compliance and performance: Evaluating suppliers based on adherence to contract terms, product quality, and responsiveness helps maintain high standards and strengthen supplier relationships. Regular supplier performance reviews ensure that only the best vendors are retained.
By consistently tracking these KPIs, businesses can identify bottlenecks, improve supplier relationships, and ensure the purchasing process supports overall organizational goals.
Conclusion
As businesses face new challenges in supply chain management, such as global disruptions and sustainability demands, they must continually evolve their purchasing strategies. From identifying needs to supplier performance evaluation, each step must be carefully managed, and integrating technology—such as automation, AI, and data analytics—can dramatically enhance the process.
At the end of the day, businesses that invest in optimizing their purchasing process will see enhanced operational efficiency, cost reductions, and stronger supplier partnerships, driving long-term success.

Webinar: From Reactive to Real-Time Spend Management
Learn why more CFOs are investing in technology and systems that deliver real-time visibility and control over all business spend – to ultimately reduce risk and cut costs.



