
Procurement Management: A Complete Guide
Procurement inefficiencies come at a steep cost for organizations.
Consider this: According to a 2024 study conducted by Impact Economist, disruptions in a company’s supply chain can result in a 10% annual revenue loss (on average).
Procurement management is more than just a back-office function; it is a strategic pillar that directly influences an organization’s operational efficiency, cost management, and competitive edge. At its core, procurement management encompasses the end-to-end processes of acquiring goods and services. This includes:
-
Identifying organizational needs
-
Sourcing vendors
-
Negotiating contracts
-
Managing supplier relationships
In an era where disruptions—from global pandemics to geopolitical tensions—can wreak havoc on supply chains, procurement has taken center stage in risk mitigation and resilience-building. The modern organization is no longer just looking for the cheapest vendor but seeking partnerships that align with long-term goals such as sustainability, innovation, and scalability. An effective procurement management strategy is key to companies remaining agile and profitable.

Download the 2024 Procurement Software Buyer’s Guide
Your guide to selecting the right procure-to-pay platform for your organization’s needs – to drive measurable process efficiency and cost savings.
Whether you’re managing direct procurement (essential materials for production) or indirect procurement (support services like IT or office supplies), an optimized procurement management process ensures that every dollar spent delivers maximum value. The rise of digital transformation has revolutionized procurement. Traditional, manual processes are giving way to procurement management systems that leverage automation, data analytics, and AI. These tools streamline workflows, provide actionable insights, and enable organizations to make faster, more informed decisions.
This guide dives deep into every aspect of procurement management, equipping you with the knowledge and tools needed to optimize your procurement processes – whether you’re a seasoned professional looking to refine your strategy or a newcomer wanting to understand the basics.
What is procurement management?
At its most fundamental level, procurement management is acquiring the goods and services an organization needs to achieve its objectives. However, it goes far beyond simply “buying things.” Procurement management is a strategic approach that ensures purchases are aligned with business goals, budgets, and timelines while fostering strong supplier relationships and maintaining compliance with regulations. It encompasses a full spectrum of activities, from identifying requirements to managing supplier contracts and mitigating risks.
Whether sourcing raw materials for manufacturing or negotiating contracts for IT services, a well-executed procurement strategy can lower costs, ensure consistent quality, and reduce disruptions.
Procurement vs. purchasing: a key distinction
While “procurement” and “purchasing” are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct processes. Purchasing focuses primarily on the transactional aspects, such as placing orders and making payments. Procurement, on the other hand, takes a holistic view, encompassing strategic sourcing, supplier selection, contract management, and performance evaluation.
For example:
-
Purchasing: Ordering office supplies through a vendor.
-
Procurement: Evaluating multiple vendors, negotiating favorable terms, ensuring sustainability, and monitoring supplier performance.
Understanding this distinction is crucial to building a comprehensive procurement management process that delivers long-term value.
Here, we go into more detail on procurement vs purchasing.
The core objectives of procurement management
A successful procurement management strategy aims to achieve the following:
-
Cost efficiency: Secure the best value for money by optimizing spending and reducing unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality assurance: Ensure all purchased goods and services meet organizational standards.
-
Timely delivery: Avoid project delays by ensuring reliable delivery of goods and services.
-
Risk mitigation: Identify and address potential risks in supplier relationships, compliance, and market conditions.
-
Sustainability and ethics: Promote responsible sourcing practices that align with environmental and social governance goals.
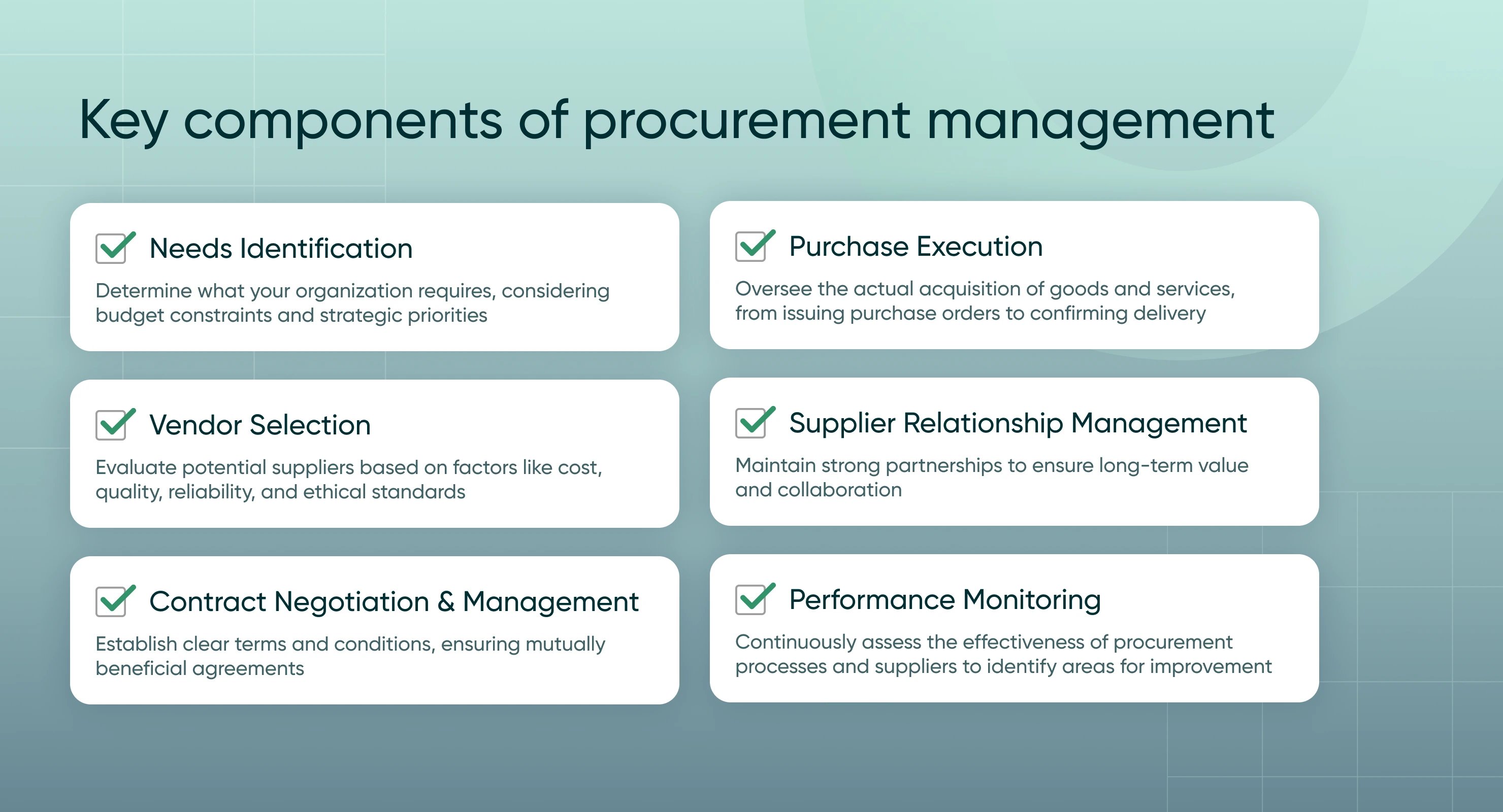
Key components of procurement management
To better understand procurement management, let’s break it down into its main components:
-
Needs identification: Determine what your organization requires, considering budget constraints and strategic priorities.
-
Vendor selection: Evaluate potential suppliers based on factors like cost, quality, reliability, and ethical standards.
-
Contract negotiation and management: Establish clear terms and conditions, ensuring mutually beneficial agreements.
-
Purchase execution: Oversee the actual acquisition of goods and services, from issuing purchase orders to confirming delivery.
-
Supplier relationship management: Maintain strong partnerships to ensure long-term value and collaboration.
-
Performance monitoring: Continuously assess the effectiveness of procurement processes and suppliers to identify areas for improvement.
The growing importance of procurement management
The role of procurement management has evolved significantly in recent years – shifting from a back-office function to a strategic enabler of organizational success. As supply chains become more globalized and complex, organizations face increasing pressure to manage costs, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance.
Moreover, businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing, requiring procurement teams to consider factors like environmental impact, labor practices, and supplier diversity when making decisions. With the rise of procurement management systems, technology now plays a crucial role in achieving these goals by automating workflows, improving data visibility, and enabling real-time decision-making.
The procurement management process
A successful procurement management strategy is built on a well-defined process that ensures efficiency, compliance, and value at every step. This structured approach helps organizations systematically identify needs, source suppliers, and manage purchases to achieve their operational and strategic goals. Below, we break down the procurement management process into seven key stages.
1. Planning and needs identification
The procurement process begins with identifying what your organization needs to purchase and planning how to fulfill those needs. This involves:
-
Determining requirements: Collaborating with departments to assess the quantity, quality, and timing of required goods or services.
-
Budget alignment: Ensuring that purchases fit within budget constraints and align with organizational goals.
-
Stakeholder input: Engaging stakeholders early to avoid misaligned expectations.
A manufacturing company, for example, may identify a need for new machinery to improve production capacity. Planning involves estimating costs, researching market availability, and setting project timelines.
2. Vendor selection and sourcing
Choosing the right suppliers is critical to achieving procurement objectives. This stage involves:
-
Market research: Identifying potential vendors that meet your organization’s requirements.
-
Evaluation criteria: Assessing vendors based on cost, quality, reliability, and compliance with ethical or sustainability standards.
-
Request for proposals (RFPs): Issuing RFPs or requests for quotations (RFQs) to solicit competitive bids from vendors.
-
Shortlisting: Narrowing down options based on vendor responses and past performance.
It is a good idea to leverage procurement management systems to automate vendor comparison and streamline sourcing decisions.
3. Contract negotiation and management
Once a vendor is selected, the next step is to negotiate a mutually beneficial agreement. This involves:
-
Defining terms: Outlining delivery schedules, payment terms, warranties, and performance expectations.
-
Mitigating risks: Including clauses that protect your organization, such as penalties for late deliveries or non-compliance.
-
Formalizing agreements: Drafting and signing contracts that comply with legal and regulatory standards.
Remember that contracts should be dynamic documents—periodically reviewed and updated as needed to adapt to changing circumstances.
4. Purchase execution
This is the transactional phase where the organization formally procures the goods or services. Key activities include:
-
Issuing purchase orders (POs): Officially requesting goods or services from the vendor.
-
Approval workflow: Ensuring purchase orders go through the appropriate approval process to prevent unauthorized spending.
-
Vendor communication: Maintaining clear communication to confirm order details and timelines.
Modern procurement management systems simplify this phase by automating PO generation and tracking.
5. Receiving and quality control
Once the goods or services are delivered, they must be inspected and verified to ensure they meet agreed-upon standards. Activities include:
-
Inspection: Checking that items match the specifications in the PO and contract.
-
Documentation: Recording receipts and resolving discrepancies (e.g., incorrect quantities or defects).
-
Feedback loop: Communicating issues to suppliers for resolution.
For example, a retailer receiving a shipment of clothing inspects items for defects and verifies quantities against the PO before approving payment.
6. Payment and reconciliation
Timely and accurate payment is essential for maintaining strong supplier relationships. This stage involves:
-
Invoice verification: Matching invoices with POs and delivery records to ensure accuracy.
-
Payment approval: Following internal approval workflows to authorize payments.
-
Timely payment: Processing payments within agreed-upon terms to avoid late fees and maintain trust.
It’s best practice to use accounts payable automation tools to streamline invoice processing and reduce errors.
7. Performance review and supplier management
The final stage of the process focuses on evaluating procurement outcomes and building long-term supplier relationships. This includes:
-
Performance metrics: Assessing suppliers based on delivery reliability, quality, and responsiveness.
-
Continuous improvement: Identifying areas for process optimization or renegotiating terms for better value.
-
Supplier collaboration: Fostering partnerships to drive innovation and mutual growth.
Leverage procurement analytics to identify trends, risks, and opportunities for continuous improvement.
Why a defined procurement process matters
A clearly structured procurement management process ensures:
-
Operational efficiency: Streamlined workflows reduce delays and redundancies.
-
Cost savings: Competitive sourcing and rigorous quality control optimize spending.
-
Risk mitigation: Robust contracts and compliance reduce exposure to supplier risks.
-
Scalability: A standardized process supports growth as procurement demands increase.
By mastering these stages, organizations can unlock the full potential of procurement management, driving both immediate savings and long-term strategic value.
Procurement management systems: a game-changer
Manual procurement processes can currently no longer keep up with the demands of efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. This is where procurement management systems come into play. These technology-driven solutions automate and streamline procurement workflows, providing organizations with the tools they need to make smarter purchasing decisions, reduce errors, and optimize costs.
What is a procurement management system?
A procurement management system is a software platform designed to manage the entire procurement lifecycle, from requisitioning to payment. It integrates with other business tools, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to provide a centralized solution for managing purchases, tracking spend, and maintaining supplier relationships.
Key capabilities include:
-
Automating repetitive tasks: Streamlining approvals, purchase order (PO) generation, and invoice matching.
-
Providing real-time data: Offering insights into spending patterns and supplier performance.
-
Enhancing compliance: Ensuring adherence to internal policies and external regulations.
Key features of procurement management systems
The most effective procurement management systems are equipped with features that address the unique challenges of procurement. Here’s a closer look at the capabilities that set these tools apart:
-
Requisition and approval workflow automation:
- Enable employees to submit purchase requests with predefined forms and templates.
- Route requests through customizable approval workflows for faster decision-making.
-
Supplier management:
- Maintain a centralized database of supplier information, including certifications, performance history, and compliance records.
- Track supplier performance to identify top-performing vendors and flag potential risks.
-
Purchase order (PO) management:
- Generate POs automatically based on approved requisitions.
- Track PO statuses in real-time to ensure on-time delivery.
-
Spend analytics:
- Gain insights into spending patterns by department, category, or vendor.
- Identify opportunities for cost savings and process optimization.
-
Integration with ERP and accounting systems:
- Seamlessly connect with platforms like QuickBooks, NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics to synchronize financial data and ensure accurate reporting.
-
Compliance and audit trails:
- Enforce procurement policies automatically and maintain detailed logs for audits.
-
Mobile accessibility:
- Allow stakeholders to approve requests, review POs, and track spending from anywhere, on any device.
Benefits of using a procurement management system
Investing in a procurement management system delivers significant benefits across multiple dimensions.

-
Efficiency and productivity:
Automating manual tasks such as data entry, approval routing, and invoice matching reduces administrative workload, enabling your team to focus on strategic initiatives.
-
Cost savings:
With better visibility into spending and access to analytics, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities, such as consolidating suppliers or negotiating volume discounts.
-
Risk reduction:
Centralized supplier data and automated compliance tracking minimize the risk of working with unreliable vendors or violating regulations.
-
Improved accuracy:
By eliminating manual data entry, procurement management systems reduce the risk of errors that can lead to costly discrepancies.
-
Scalability:
These systems can handle increasing procurement demands as your organization grows, ensuring consistent processes and results.
-
Enhanced transparency:
Real-time reporting provides stakeholders with visibility into procurement activities, fostering accountability and informed decision-making.
Top procurement management systems to consider
When selecting a procurement management system, choosing one that aligns with your organization’s needs is essential. Here are some leading options:
-
Procurify:
Known for its user-friendly interface, AI and automation capabilities, real-time spend tracking, and seamless integrations with ERP systems like QuickBooks and NetSuite.
-
SAP Ariba:
Offers comprehensive features for global enterprises, including supplier collaboration and contract management.
-
Coupa:
A robust solution with advanced analytics and AI-powered insights for spend optimization.
-
Zycus:
Focuses on AI-driven procurement, automating tasks like supplier evaluation and invoice processing.
Benefits of effective procurement management
Effective procurement management is more than a cost-cutting measure—it’s a strategic enabler that drives value, enhances efficiency, and builds resilience across an organization. When done right, procurement management delivers benefits that ripple throughout the business, impacting everything from operational processes to long-term competitiveness. Let’s explore the key advantages in detail.
1. Cost efficiency
Procurement management’s most immediate and measurable benefit is cost savings. By optimizing the procurement process, organizations can reduce unnecessary expenses, negotiate better contracts, and consolidate suppliers for volume discounts.
Here are three ways to achieve cost efficiency:
-
Competitive bidding – ensures the best price for goods and services.
-
Spend analytics – identifies cost-saving opportunities and flags areas of overspending.
-
Strategic sourcing – consolidates purchasing power for improved terms and pricing.
2. Enhanced risk management
Procurement management helps organizations identify and mitigate risks, such as unreliable suppliers, compliance violations, or market disruptions. With robust processes in place, businesses can anticipate and address issues before they escalate.
Three ways you can enhance risk management:
-
Supplier vetting – reduces the likelihood of engaging with underperforming or non-compliant vendors.
-
Contract management – ensures terms protect the organization from risks like late deliveries or price fluctuations.
-
Procurement systems – provide real-time visibility into supply chain vulnerabilities.
Future-proofing tip: Diversify suppliers geographically to reduce exposure to regional risks, such as natural disasters or political instability.
3. Operational efficiency
Streamlined procurement workflows eliminate bottlenecks and reduce administrative burdens, enabling faster, more accurate purchases. This ensures that goods and services are delivered on time, avoiding costly delays.
How operational efficiency works:
-
Automated purchase requests and approvals – minimize manual effort and shorten cycle times.
-
Centralized supplier databases – make it easier to manage relationships and track performance.
-
Procurement management systems – integrate with ERP tools for seamless order-to-payment workflows.
4. Quality assurance
Procurement management ensures that the goods and services acquired meet quality standards, which is vital for maintaining customer satisfaction and operational excellence.
Aspects of quality assurance:
-
Supplier performance monitoring – tracks quality metrics over time, flagging issues early.
-
Contracts – include detailed specifications to ensure compliance with quality requirements.
-
Inspection protocols at the receiving stage – catch defects or discrepancies before they impact operations.
The result is better quality control means fewer returns, less rework, and more reliable production schedules.
5. Improved supplier relationships
Strong supplier relationships are the foundation of a resilient procurement strategy. Procurement management fosters collaboration and trust, enabling businesses to negotiate better terms, access priority services, and foster innovation.
How it works:
-
Transparent communication – builds mutual trust and ensures alignment on expectations.
-
Long-term contracts – incentivize suppliers to prioritize your organization over competitors.
-
Performance reviews and feedback – help suppliers improve and maintain standards.
It is best practice to engage in strategic partnerships with suppliers who align with your business values, such as sustainability or innovation.
6. Increased compliance and governance
Procurement management ensures that all purchasing activities align with internal policies, industry regulations, and legal requirements. This reduces the risk of fines, reputational damage, or supply chain disruptions.
How it works:
-
Procurement systems – enforce approval workflows and purchasing limits automatically.
-
Audit trails – provide detailed records for internal and external audits.
-
Regulatory compliance – is built into contract templates and vendor selection criteria.
It is recommended to use procurement analytics to monitor compliance trends and proactively address potential gaps.
7. Sustainability and ethical sourcing
Modern businesses are under increasing pressure to prioritize environmental and social responsibility in their procurement practices. Effective procurement management helps organizations align with sustainability goals while supporting fair labor practices and reducing their carbon footprint.
The main aspects of sustainability and ethical sourcing:
-
Vendor evaluations – include criteria for sustainability certifications and ethical practices.
-
Spend analytics – identify opportunities to source from eco-friendly suppliers or reduce waste.
-
Long-term sourcing strategies – focus on renewable materials and reduced environmental impact.
8. Data-driven decision making
Procurement management relies on data analytics to inform decisions, uncover trends, and improve processes. With access to real-time data, organizations can make smarter, faster choices that align with their goals.
How it works:
-
Spend analytics – reveal cost-saving opportunities and flag inefficient processes.
-
Supplier performance dashboards – help identify high-performing and underperforming vendors.
-
Predictive analytics – anticipate market trends and support proactive sourcing strategies.
Businesses using procurement analytics typically achieve cost savings (up to 22%) more often than those relying on manual processes.
The bottom line
The benefits of effective procurement management extend far beyond cost savings. It’s a strategic approach that drives operational excellence, enhances supplier collaboration, and builds resilience in an increasingly volatile business environment. By optimizing procurement processes, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, deliver consistent quality, and align with broader goals such as sustainability and risk mitigation.
Challenges in procurement management and how to overcome them
Procurement management is not without its challenges. They often encounter obstacles ranging from supplier risks to technological gaps. The good news? With the right strategies and tools, these challenges can be effectively managed or even transformed into opportunities for growth. Let’s explore the most common challenges in procurement management and actionable solutions.
1. Supplier reliability and performance issues
The challenge: Ensuring supplier reliability is a perennial challenge in procurement. Late deliveries, substandard products, or sudden supplier failures can disrupt operations and lead to significant financial losses.
The solution:
-
Thorough vetting: Conduct rigorous supplier evaluations during the selection process, considering financial stability, past performance, and certifications.
-
Performance monitoring: Use procurement management systems to track supplier performance metrics (e.g., on-time delivery, and defect rates).
-
Diversified sourcing: Avoid over-reliance on a single supplier by maintaining a diverse vendor portfolio.
Pro tip: Build strong relationships with key suppliers to encourage collaboration and prioritize your organization during high-demand periods.
2. Lack of spend visibility
The challenge: Many organizations struggle with fragmented data and limited visibility into their spending patterns. This can lead to overspending, maverick purchasing (unauthorized buying), and missed cost-saving opportunities.
The solution:
-
Centralized procurement tools: Implement a procurement management system that consolidates all procurement data in one place.
-
Spend analytics: Leverage data visualization tools to analyze spending trends, identify inefficiencies, and uncover savings opportunities.
-
Policy enforcement: Establish clear procurement policies and ensure compliance across all departments.
3. Managing supplier relationships
The challenge: Balancing relationships with multiple suppliers while maintaining leverage in negotiations can be difficult. Poor communication or lack of trust can lead to conflicts and missed opportunities.
The solution:
-
Strategic collaboration: Treat key suppliers as partners rather than transactional entities. Share forecasts and collaborate on long-term goals.
-
Supplier feedback loops: Regularly provide performance feedback and request suggestions for mutual improvement.
-
Vendor relationship management tools: Use technology to maintain comprehensive supplier profiles and communication records.
Best practice: Organize periodic supplier performance reviews to align expectations and reinforce collaboration.
4. Compliance and regulatory risks
The challenge: Organizations must navigate complex legal, ethical, and environmental regulations. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, legal disputes, or reputational damage.
The solution:
-
Standardized contracts: Use templates that include clauses addressing regulatory requirements, sustainability goals, and legal protections.
-
Real-time compliance monitoring: Automate compliance tracking using procurement software with built-in alerts for policy or regulatory violations.
-
Training: Ensure procurement teams are well-versed in relevant regulations and industry standards.
Stay updated on emerging regulations, such as ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) standards, to remain compliant and competitive.
5. Inefficient procurement processes
The challenge: Manual, disjointed workflows can lead to delays, errors, and frustration for procurement teams. Slow approval processes and lack of integration with other systems exacerbate inefficiencies.
The solution:
-
Process automation: Automate repetitive tasks like approval routing, purchase order generation, and invoice matching.
-
Integration with ERP systems: Connect procurement tools with enterprise resource planning systems for seamless data flow and reduced manual effort.
-
Streamlined workflows: Use workflow optimization to eliminate unnecessary steps and shorten procurement cycles.
6. Controlling procurement costs
The challenge: Rising costs and unanticipated expenses can undermine the effectiveness of procurement strategies. Poor negotiation practices and fragmented supplier contracts contribute to this issue.
The solution:
-
Data-driven negotiations: Use spend data to negotiate better terms with suppliers.
-
Supplier consolidation: Work with fewer suppliers to take advantage of bulk discounts and economies of scale.
-
Regular budget reviews: Periodically review and adjust procurement budgets to account for market changes.
Pro tip: Set up cost benchmarking practices to compare supplier pricing against market averages.
7. Adapting to technological change
The challenge: The rapid evolution of technology means organizations must continuously upgrade their tools and processes to stay competitive. Resistance to change or lack of expertise can slow down adoption.
The solution:
-
Phased implementation: Roll out new technology in stages to minimize disruption and allow employees to adapt.
-
Training programs: Invest in regular training sessions to upskill procurement teams.
-
Future-proof tools: Choose scalable procurement systems that integrate emerging technologies like AI and blockchain.
8. Supply chain disruptions
The challenge: Global supply chains are increasingly vulnerable to disruptions caused by geopolitical events, natural disasters, or pandemics. Such disruptions can delay deliveries and inflate costs.
The solution:
-
Scenario planning: Develop contingency plans for potential disruptions, including backup suppliers and alternative shipping routes.
-
Supplier diversification: Source from multiple suppliers across different regions to mitigate geographic risks.
-
Real-time tracking: Use procurement systems with supply chain visibility features to monitor orders and identify potential bottlenecks.
Consider adopting predictive analytics tools to forecast disruptions and adjust procurement strategies proactively.
Turning challenges into opportunities
Procurement management challenges can feel daunting, but they also present opportunities for growth, innovation, and competitive differentiation. By addressing these issues head-on with a mix of strategic planning, technological investment, and continuous improvement, organizations can transform their procurement function into a driver of value and resilience.
In the next section, we’ll explore best practices to further optimize your procurement processes and maximize your outcomes.
Procurement management best practices
Implementing best practices in procurement management can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and mitigate risks. Whether you’re fine-tuning an existing strategy or building one from scratch, these proven practices provide a strong foundation for optimizing procurement processes and delivering long-term value.
1. Develop a strategic procurement plan
Why it matters: A strategic plan aligns procurement activities with organizational goals, ensuring that every purchase contributes to broader business objectives.
How to do it:
-
Define clear procurement objectives, such as cost savings, sustainability goals, or supplier diversity.
-
Analyze historical spending data to identify trends and areas for improvement.
-
Collaborate with stakeholders across departments to understand their needs and priorities.
Pro tip: Use spend analysis tools to establish benchmarks and track progress against goals.
2. Build strong supplier relationships
Why it matters: Healthy supplier relationships are crucial for reliable deliveries, quality assurance, and cost control. A collaborative approach fosters trust and innovation.
How to do it:
-
Communicate regularly to ensure alignment on expectations and timelines.
-
Recognize and reward top-performing suppliers with preferred partnerships or extended contracts.
-
Involve suppliers in long-term planning to encourage mutual growth.
Companies with strong supplier relationships experience fewer disruptions during supply chain crises.
3. Prioritize data-driven decision making
Why it matters: Decisions based on real-time data are more accurate and impactful than those relying on intuition or outdated information.
How to do it:
-
Leverage procurement analytics to monitor spending, track supplier performance, and identify inefficiencies.
-
Use predictive analytics to anticipate market trends and plan purchases strategically.
-
Set up dashboards for a bird’s-eye view of procurement KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
Remember to focus on metrics like cost savings, cycle time reduction, and supplier compliance rates.
4. Standardize and automate procurement workflows
Why it matters: Standardized workflows reduce errors, improve compliance, and streamline processes, while automation eliminates repetitive tasks, saving time and effort.
How to do it:
-
Create standardized templates for requisitions, purchase orders, and contracts.
-
Automate approval workflows to ensure purchases are reviewed and approved quickly.
-
Use procurement management systems to centralize processes and reduce administrative overhead.
5. Enforce compliance and governance
Why it matters: Strict compliance with policies and regulations mitigates legal and reputational risks while ensuring ethical and sustainable sourcing practices.
How to do it:
-
Develop clear procurement policies and communicate them to all stakeholders.
-
Use procurement tools to enforce spending limits, approval hierarchies, and contract terms automatically.
-
Regularly audit procurement processes and supplier performance to ensure adherence to regulations.
Incorporate sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards into your procurement policies.
6. Embrace technology and digital tools
Why it matters: Modern procurement tools enhance visibility, streamline operations, and provide actionable insights for decision-making.
How to do it:
-
Adopt a procurement management system to automate routine tasks and integrate with other tools like ERPs.
-
Leverage cloud-based solutions for remote accessibility and real-time updates.
-
Explore emerging technologies like AI and blockchain for predictive analytics and enhanced security.
Pro tip: Choose scalable technology that can grow with your organization’s procurement needs.
7. Focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing
Why it matters: Sustainability and ethics are increasingly important to consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies. Responsible sourcing strengthens your brand and aligns with global trends.
How to do it:
-
Evaluate suppliers based on environmental impact, labor practices, and certifications.
-
Set sustainability goals, such as reducing carbon emissions or sourcing renewable materials.
-
Educate your team on ethical procurement standards to ensure compliance.
8. Train and empower your procurement team
Why it matters: A well-trained team is better equipped to make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and adapt to new challenges.
How to do it:
-
Provide ongoing training on procurement technologies, negotiation skills, and compliance requirements.
-
Empower team members to take ownership of procurement projects and suggest improvements.
-
Foster a culture of collaboration between procurement and other departments.
Encourage team members to earn certifications like CPSM (Certified Professional in Supply Management) for professional development.
9. Regularly review and optimize procurement processes
Why it matters: Continuous improvement ensures your procurement strategy evolves with business needs and market conditions.
How to do it:
-
Conduct regular process reviews to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
-
Solicit feedback from stakeholders and suppliers to uncover opportunities for improvement.
-
Benchmark performance against industry standards to remain competitive.
10. Plan for disruptions and build resilience
Why it matters: Global supply chains are vulnerable to disruptions, from natural disasters to geopolitical crises. A proactive approach ensures continuity.
How to do it:
-
Develop contingency plans, including backup suppliers and alternative logistics options.
-
Diversify supplier networks to avoid over-reliance on any single vendor.
-
Use predictive analytics to anticipate disruptions and adjust procurement strategies in advance.
Future-ready tip: Partner with suppliers who have robust risk management practices in place.
The bottom line
Implementing these best practices empowers organizations to turn procurement management into a strategic asset. From fostering supplier partnerships to leveraging cutting-edge technology, these strategies address common challenges and position procurement as a driver of efficiency, sustainability, and competitive advantage.
FAQs about procurement management
To help address common questions about procurement management, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions. These answers provide clarity on key concepts and practical advice for businesses seeking to enhance their procurement processes.
So what?
If your organization still relies on spreadsheets or manual workflows, implementing a procurement management system could be the key to unlocking efficiency, cost savings, and strategic value. As procurement becomes increasingly central to business success, investing in the right tools is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Adopting a robust procurement management system allows your organization to streamline operations and stay ahead in a competitive marketplace. The result? Stronger supplier relationships, more effective use of resources, and greater organizational agility.
As businesses increasingly prioritize agility, data-driven decisions, and ethical sourcing, procurement management will continue to evolve and grow in importance. Organizations that invest in this critical function today will position themselves to adapt to future challenges, seize new opportunities, and lead in their industries.

2025 Spend Management Software Buyer’s Guide
Choose the spend management solution best suited to your organization’s needs with an overview of the 2025 software ecosystem, feature comparisons, and a free vendor capability evaluation checklist.
