Mastering Invoice Management: Streamline Your Cash Flow
The start of a new year always signals the opportunity for a fresh start.
If you are part of an accounts payable and procurement team aiming to improve your processes and maximize your saving opportunities, then building a strong invoice management strategy is a great place to start.
Invoice management is the process of handling, tracking, and processing invoices from receipt to payment, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and timely settlement. It is pivotal in maintaining a company’s financial health and operational efficiency. By enabling clear visibility into incoming and outgoing payments, invoice management helps businesses manage cash flow effectively and avoid disruptions in vendor relationships.
However, this is not a simple process to master. Many organizations face significant challenges with inefficient invoice management processes. Manual handling often leads to:
-
Delays
-
Data entry errors
-
Lost invoices
These pain points disrupt cash flow and strain supplier trust. Compliance risks are another common issue, as missing invoices or inaccurate reporting can result in audits or financial penalties. Additionally, the lack of real-time insights makes it difficult for businesses to forecast expenses and make informed financial decisions.
Invoice automation software offers a transformative approach to these challenges. By digitizing and streamlining invoice workflows, automation reduces manual effort, enhances accuracy, and ensures compliance. These tools accelerate the invoice-to-payment cycle and provide valuable procurement analytics that empower businesses to optimize their financial strategies.
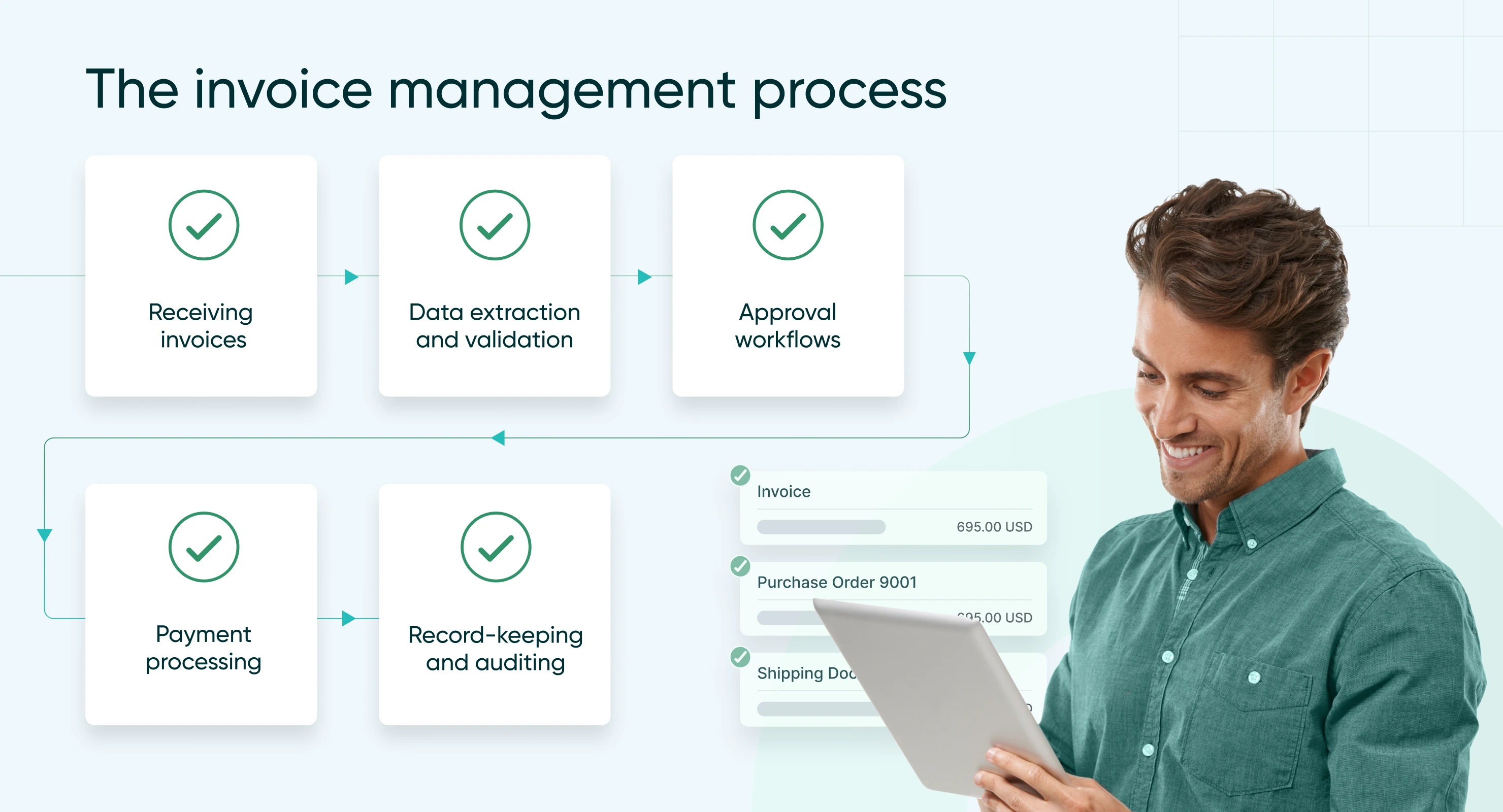
The invoice management process
Effective invoice management involves several critical steps that ensure invoices are processed accurately, efficiently, and in compliance with regulations.
-
Receiving invoices
Invoices are received through various channels, including email, physical mail, and electronic data interchange (EDI). Each method has its unique challenges:
- Email: Invoices in PDF or other formats can easily be overlooked or misfiled without a centralized system.
- Physical Mail: Paper invoices can be lost or delayed in transit, requiring manual input that increases the risk of errors.
- EDI: While efficient for exchanging data between systems, EDI setups can face issues with incompatible formats or incomplete fields.
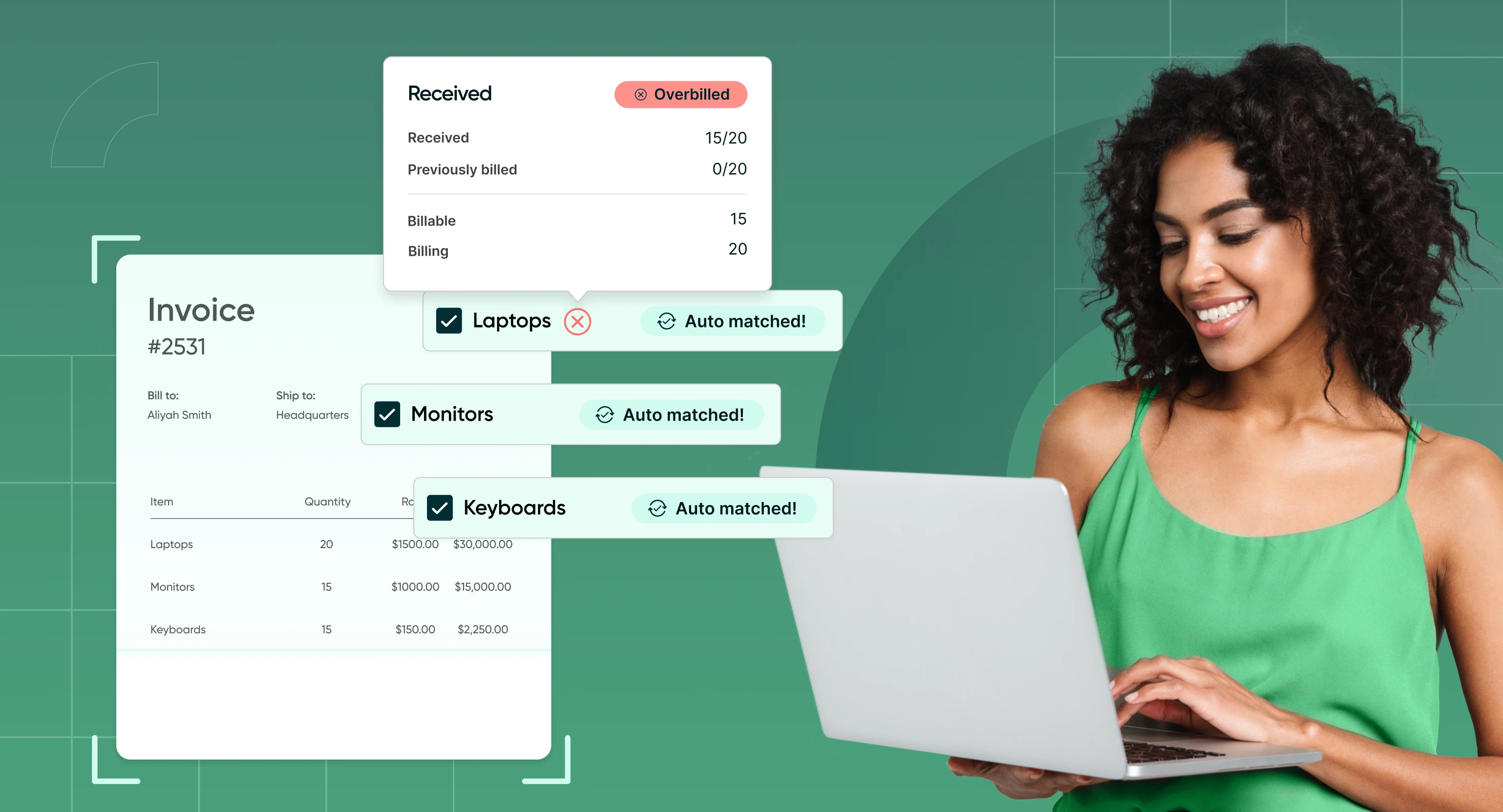
A common pain point during this stage is the receipt of invoices with missing information, such as incorrect PO numbers, mismatched totals, or incomplete supplier details. These discrepancies can delay processing and disrupt payment timelines.
-
Data extraction and validation
Accurate data extraction is critical to avoid errors in processing. This step typically involves verifying key details such as:
- PO numbers and contract terms.
- Supplier information and bank account details.
- Invoice amounts, taxes, and line-item details.
Modern tools like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) can automatically extract data from digital invoices, reducing the need for manual input and improving accuracy. More advanced systems use AI-powered data validation to flag discrepancies, ensuring that invoices align with purchase orders and contracts before moving to the next stage.
-
Approval workflows
Defined approval workflows ensure invoices are reviewed and authorized promptly, avoiding bottlenecks and ensuring timely payments. These workflows typically involve stakeholders such as finance teams, procurement staff, and department heads.
- Clear roles and responsibilities prevent delays and ensure compliance with company policies.
- Automated approval processes can route invoices to the correct stakeholders based on pre-defined rules, such as invoice amount or department.
By leveraging automated workflows, businesses can significantly reduce approval cycle times and eliminate the risk of overlooked invoices.
-
Payment processing
Once an invoice is approved, the next step is scheduling and executing payments. Effective payment processing involves:
- Managing payment terms: Optimizing cash flow by adhering to agreed-upon terms or negotiating early payment discounts with suppliers.
- Automated payments: Using electronic payment systems to ensure payments are made accurately and on time.
Automation helps reduce late payment penalties, strengthens supplier relationships, and minimizes manual intervention, enabling smoother financial operations.
-
Record-keeping and auditing
Maintaining detailed records of invoices is essential for tax compliance and regulatory audits. Organized records help businesses:
- Prove compliance with legal and tax obligations.
- Streamline audits by providing easy access to historical data.
Digital archiving systems simplify record-keeping by storing invoices in centralized, searchable databases. This ensures that financial documents are compliant and easily accessible for internal reviews or external audits.
Challenges in invoice management
While invoice management is a critical function for businesses, many organizations face persistent challenges that can disrupt financial operations and damage supplier relationships. Below are some of the most common obstacles and their impact.
-
Manual processing errors
Manual invoice processing is prone to human errors, such as:
- Data entry mistakes: Incorrect amounts, mismatched PO numbers, or typos in supplier information.
- Duplicate payments: Paying the same invoice twice due to oversight or lack of a centralized tracking system.
These errors compromise financial accuracy, leading to issues like overpayments, underpayments, or misaligned budgets. Additionally, repeated errors can harm supplier trust, potentially affecting contract negotiations or causing disruptions in the supply chain.
-
Delayed approvals
Approval delays often stem from inefficient workflows, including:
- Lack of centralized systems: Invoices get stuck in email chains or paper trails.
- Unclear responsibilities: Without defined roles, approvals can languish due to confusion over who needs to take action.
These delays can disrupt payment schedules, resulting in late fees, strained supplier relationships, and missed opportunities for early payment discounts. They also impede cash flow planning, making it harder for businesses to maintain liquidity.
-
Fraud risks
Invoice fraud is a growing concern, with examples including:
- Fake invoices: Fraudsters submit invoices that appear to be from legitimate suppliers.
- Phishing attacks: Scams that trick employees into sharing sensitive payment information or processing fraudulent payments.
Mitigating fraud risks requires a combination of authentication tools (e.g., validating supplier credentials and verifying invoice details) and employee training to recognize red flags like unexpected payment requests or unfamiliar bank accounts.
-
Lack of visibility and reporting
Manual processes often lead to siloed data, where critical invoice information is scattered across different departments or systems. This lack of integration results in:
- Limited oversight: Finance teams struggle to get a clear view of outstanding invoices, payment statuses, and overall cash flow.
- Missed insights: Businesses cannot identify trends or inefficiencies in their invoice processing without proper reporting.
Real-time dashboards can address these challenges by providing centralized visibility into invoice statuses, payment timelines, and financial metrics. This enables organizations to make informed decisions, identify bottlenecks, and improve financial planning.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, businesses can transition from inefficient, error-prone processes to streamlined systems that enhance financial accuracy, supplier trust, and operational efficiency.
Modern solutions and best practices in invoice management
Adopting modern solutions and best practices can significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and security of invoice management processes. Below, we explore the key strategies and technologies transforming the field.
-
Implementing accounts payable (AP) automation
AP automation tools streamline invoice workflows by automating time-consuming tasks such as data entry, invoice matching, and routing for approvals. Key capabilities include:
- Automatic matching: Ensuring invoices align with purchase orders and receipts.
- Smart routing: Directing invoices to the appropriate stakeholders based on predefined rules.
The ROI on AP automation is substantial, including reduced processing times, fewer errors, and lower administrative costs. For example, businesses can cut invoice processing time from weeks to days, allowing for faster payments and improved supplier relationships.
-
Adopting electronic invoicing systems
Transitioning to electronic invoicing (e-invoicing) eliminates many inefficiencies of paper-based processes. Key benefits include:
- Cost savings: Lower printing, mailing, and storage expenses.
- Improved compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements for digital record-keeping.
- Speed: Faster invoice receipt and processing.
Standards like PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online) ensure interoperability for cross-border e-invoicing, making it easier to comply with global trade requirements.
-
Utilizing invoice processing software
Modern invoice processing software offers advanced features that enhance scalability and integration with existing systems. When selecting a platform, businesses should prioritize:
- Scalability: The ability to handle increasing invoice volumes as the business grows.
- Integration with ERP systems: Seamless connections to tools like QuickBooks, NetSuite, or SAP for centralized data management.
- AI-powered analytics: Identifying trends, anomalies, and optimization opportunities in invoice processing.
Popular platforms such as Procurify, SAP Concur, and Tipalti, provide end-to-end solutions that simplify the invoice-to-payment process while offering valuable insights.
-
Establishing efficient approval workflows
Efficient approval workflows eliminate bottlenecks and ensure timely invoice processing. Best practices include:
- Workflow automation tools: Platforms that enable conditional routing rules based on factors like invoice amount, department, or urgency.
- Mobile accessibility: Allowing stakeholders to review and approve invoices on the go, ensuring the process stays on track.
Automating approvals accelerates the process and improves accountability by maintaining a clear audit trail.
-
Ensuring compliance and security
Global invoicing often involves complex tax regulations such as VAT (Value-Added Tax) and GST (Goods and Services Tax). To ensure compliance, businesses should:
- Stay updated on regional tax requirements and reporting obligations.
- Leverage invoicing tools that automatically calculate and document taxes for accuracy.
Data security is equally critical in safeguarding sensitive financial information. Best practices include:
- Encryption: Protecting data during transmission and storage.
- Access controls: Limiting invoice access to authorized personnel.
- Regular audits: Monitoring for vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with cybersecurity standards.
Benefits of effective invoice management
Implementing efficient and streamlined invoice management processes delivers significant benefits across financial operations, supplier relationships, and organizational productivity. Here’s how effective invoice management can positively impact your business:

-
Improved cash flow
Efficient invoice management provides visibility into payment schedules and outstanding invoices, enabling businesses to better predict and plan for cash needs. Key benefits include:
- Accurate cash flow forecasting: Real-time tracking of incoming and outgoing payments ensures businesses can allocate resources effectively.
- Reduced days payable outstanding (DPO): By processing invoices faster and adhering to payment terms, businesses can maintain healthier financial metrics, enhancing liquidity and creditworthiness.
-
Enhanced supplier relationships
Timely and accurate payments are essential for fostering strong supplier relationships. Effective invoice management helps businesses:
- Build trust with suppliers: On-time payments demonstrate reliability, potentially leading to favorable payment terms or discounts.
- Increase transparency: Supplier portals provide vendors with real-time updates on invoice statuses, reducing the need for follow-up inquiries and improving communication.
Strong supplier relationships translate into a more resilient supply chain and better opportunities for collaboration.
-
Operational efficiency
Streamlining invoice workflows minimizes administrative burdens, allowing teams to focus on higher-value tasks. Key efficiency gains include:
- Reduced administrative overhead: Automation eliminates manual tasks like data entry and matching, saving time and resources.
- Faster cycle times: Accelerated invoice processing ensures approvals and payments happen swiftly, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall productivity.
This operational agility empowers finance teams to focus on strategic initiatives, such as budgeting, forecasting, and financial analysis.
-
Cost savings
Effective invoice management leads to both direct and indirect cost savings:
- Direct savings: Transitioning to digital processes reduces expenses on paper, printing, and postage.
- Indirect savings: Avoiding late fees or penalties and capitalizing on early payment discounts from suppliers.
By reducing processing costs and optimizing payment schedules, businesses can maximize their financial efficiency and reinvest savings into growth opportunities.
Emerging trends in invoice management
The field of invoice management is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and a growing focus on sustainability. Here’s a look at some of the most impactful trends shaping the future of invoice management.
AI and machine learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing invoice management by automating processes and uncovering insights that were previously inaccessible. Key applications include:
-
Predictive analytics: AI can analyze historical data to detect anomalies in invoices, such as duplicate entries, unusual amounts, or mismatched supplier information, helping to prevent fraud and errors before they occur.
-
Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots are increasingly used to handle invoice-related queries from suppliers and employees. These tools can provide real-time updates on invoice statuses, payment schedules, and compliance requirements, reducing the workload on finance teams.
Blockchain technology
Blockchain is emerging as a powerful tool to enhance transparency and security in invoice management. This decentralized technology offers:
-
Immutable records: Every transaction is securely logged in a tamper-proof ledger, providing a clear audit trail for invoices.
-
Improved trust: By enabling real-time verification of invoice details, blockchain reduces disputes and builds confidence between buyers and suppliers.
-
Cross-border invoicing: Blockchain facilitates seamless and secure international payments, streamlining processes for global businesses.
Sustainability initiatives
As businesses increasingly prioritize environmental responsibility, invoice management is aligning with sustainability goals through initiatives like:
-
Paperless invoicing: Transitioning to digital invoicing eliminates the need for paper, reducing waste and carbon emissions. This shift supports eco-friendly practices and aligns with customer and stakeholder expectations for sustainable operations.
-
Sustainability metrics: Advanced platforms now provide analytics on the environmental impact of invoice management practices, allowing businesses to track and improve their performance over time.
By embracing these trends, organizations can enhance the efficiency and security of their invoice management processes and position themselves as forward-thinking and environmentally conscious leaders in their industries.
Invoice Management FAQs
Implementing effective invoice management practices is crucial for maintaining financial health and operational efficiency. Here are some frequently asked questions to guide you:
So what?
In 2025, an effective invoice management strategy can unlock an organization’s operational efficiency, and supplier trust. Transitioning from manual, error-prone processes to modern, automated solutions can drastically reduce processing times, improve accuracy, and enhance compliance.
For businesses still relying on outdated methods, now is the time to audit your current processes and identify areas for improvement. Evaluate tools like accounts payable automation software, e-invoicing systems, and AI-powered analytics to discover how they can streamline your workflows and unlock cost savings.

Webinar: Automate Your AP Processes with Procurify
Learn how AP automation enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and financial visibility of your accounts payable workflows.