Essential Steps to Master Your Procurement Process Flow
The procurement process flow may not be the most talked about aspect of finance, but it is one of the most important for procurement teams seeking to maximize efficiency.
At its core, the procurement process flow is a comprehensive, step-by-step guide that organizations use to manage the acquisition of goods and services. It serves as a roadmap that outlines each phase of the procurement cycle, from identifying the need for a product or service to finalizing payments and maintaining records. By following a structured flow, businesses can ensure that their procurement activities are efficient, transparent, and aligned with broader organizational goals.
A well-defined flow is essential for several reasons. First, it enables companies to control costs by standardizing purchasing procedures, ensuring that all departments follow the same guidelines when making purchases. This standardization helps to eliminate unauthorized spending, or “maverick spending,” which can lead to unexpected costs and budget overruns.
Additionally, a streamlined procurement process helps companies build strong, long-term relationships with suppliers by clearly communicating expectations, delivery terms, and quality standards.
Beyond cost control and supplier management, procurement process flow enhances operational efficiency. Many organizations struggle with manual processes, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. By mapping out each step and automating repetitive tasks, companies can reduce bottlenecks, speed up purchase order approvals, and minimize the risk of delays in the supply chain. This not only saves time but also allows procurement teams to focus on strategic activities such as supplier evaluation, contract negotiation, and market trend analysis.

Download the 2024 Procurement Software Buyer’s Guide
Your guide to selecting the right procure-to-pay platform for your organization’s needs – to drive measurable process efficiency and cost savings.
Moreover, a well-structured procurement process flow promotes compliance. In industries with strict regulatory requirements, maintaining accurate records of all transactions, contracts, and communications is crucial for auditing purposes. A clear flow ensures that all procurement activities are properly documented and compliant with both internal policies and external regulations.
For instance, using a structured approach for tasks like three-way matching (comparing purchase orders, invoices, and delivery receipts) helps companies avoid overpayments and ensures accurate financial reporting.
As companies grow and expand their operations, managing procurement efficiently becomes increasingly complex. This complexity has led to a greater reliance on digital tools and automation, which can simplify the procurement process and enhance overall efficiency. From e-procurement platforms that streamline purchasing activities to advanced analytics that provide insights into spending patterns, technology plays a key role in modernizing procurement practices.
Whether your goal is to streamline operations, reduce costs, or improve supplier relationships, this guide aims to provide a detailed overview of the procurement process flow, breaking down each step, highlighting best practices, and offering strategies to optimize the process.
What is procurement process flow?
The procurement process flow serves as a strategic framework that guides purchasing activities, ensuring that procurement teams adhere to company policies, manage supplier relationships, and make informed decisions. The procurement process flow ensures that every purchase, from the smallest office supply to complex machinery, is managed efficiently, transparently, and cost-effectively.
At its core, the procurement process flow is about creating a consistent, repeatable procedure that organizations can rely on to manage their purchasing needs. This flow typically begins with needs identification—where a department recognizes a requirement for goods or services—and progresses through multiple stages, including supplier selection, purchase order creation, delivery management, invoice processing, and record-keeping. Each of these stages is carefully designed to address key aspects of procurement, from ensuring product quality to maintaining cost control and compliance.
A well-defined procurement process flow not only provides clarity and direction but also contributes to operational efficiency. By clearly outlining each step, organizations can streamline communication between departments, reduce manual errors, and eliminate bottlenecks that can delay purchasing decisions. For example, setting up automated approval workflows can significantly speed up the procurement cycle by reducing the time needed for purchase requisitions and approvals. Such automation also minimizes human error, ensuring that purchase orders are accurate and payments are processed correctly.
A robust procurement process flow allows companies to build strong, strategic relationships with suppliers. By standardizing the process for selecting and engaging suppliers, organizations can ensure consistency in quality, pricing, and delivery terms. This approach enables businesses to negotiate better terms, consolidate orders for cost savings, and develop long-term partnerships that benefit both parties. Additionally, regular evaluation of supplier performance, which is often integrated into the procurement flow, helps businesses monitor and maintain high standards.
Another critical element of procurement process flow is cost control and compliance. Organizations must manage budgets carefully, and a structured flow ensures that all purchasing activities are tracked and aligned with the company’s financial goals. Using tools such as purchase orders, invoice matching, and contract management systems helps prevent unauthorized spending and ensures that all purchases comply with internal policies and external regulations. This is particularly important for companies operating in heavily regulated industries, where maintaining accurate records for audits and regulatory compliance is essential.
Ultimately, the procurement process flow is about creating a transparent, efficient, and strategic procurement environment. By implementing a structured flow, organizations can gain better visibility into their spending patterns, identify opportunities for savings, and enhance supplier management. The benefits extend beyond the procurement department; a well-functioning procurement process can drive overall business success by ensuring that resources are allocated wisely, budgets are managed effectively, and operations run smoothly.
In today’s digital age, many organizations are turning to e-procurement systems and software to enhance their procurement process flows. These systems automate repetitive tasks, provide real-time data analytics, and offer centralized platforms for managing supplier information, contracts, and purchasing activities. By leveraging technology, companies can not only streamline their procurement operations but also gain valuable insights that help them make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Breakdown of the procurement process flow
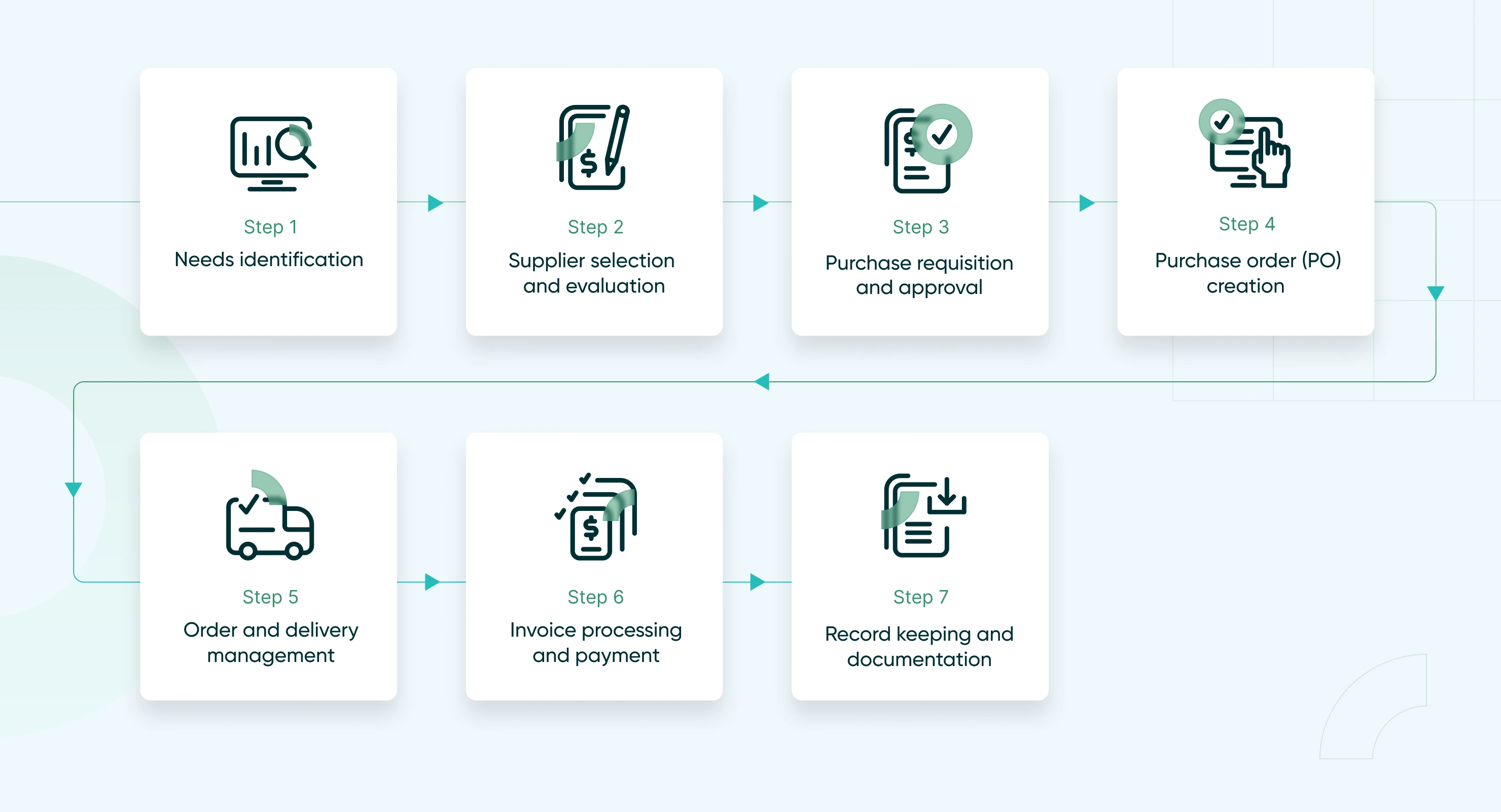
The procurement process flow can be broken down into several key stages, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring that the acquisition of goods and services is managed efficiently and strategically. These steps are designed to streamline purchasing, optimize supplier relationships, and ensure compliance with internal and external regulations. Below is a comprehensive step-by-step guide to the main stages of the procurement process flow:
-
Needs identification
The procurement process begins with the identification of a need. This could be a request for office supplies, raw materials for production, or specialized services. During this phase, it’s important to determine the exact requirements, including the quantity, quality specifications, and delivery timelines. Needs identification often involves collaboration between departments to ensure that purchases align with organizational goals and budget constraints.
Engage with key stakeholders early to gather detailed information on requirements. This helps avoid delays and ensures that the procurement team understands the specifications needed for the products or services.
-
Supplier selection and evaluation
Once the need is identified, the next step is to find suitable suppliers. This involves conducting market research, soliciting bids or proposals, and evaluating potential vendors based on criteria such as price, quality, reliability, and delivery terms. Supplier selection is a strategic decision, as building strong, long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to cost savings, improved quality, and reduced risk.
Implement strategic sourcing practices, which involve evaluating suppliers not just on cost but on their ability to meet long-term business needs. Regularly assess supplier performance to ensure they continue to meet expectations.
-
Purchase requisition and approval
Once a supplier is selected, the procurement team or the requesting department creates a purchase requisition. This document outlines the details of the intended purchase, including the item description, quantity, and preferred suppliers. The requisition is then submitted for internal approval. Depending on the organization’s structure, this may involve multiple levels of review to ensure budget alignment and compliance with procurement policies.
Utilize digital requisition systems that can automate the approval process. This reduces delays and allows for easier tracking and management of purchase requests.
-
Purchase order (PO) creation
After the purchase requisition is approved, the procurement team issues a purchase order (PO) to the chosen supplier. The PO is a formal document that serves as a legally binding contract, detailing the agreed terms of the purchase, including product specifications, delivery dates, and payment terms. At this stage, it’s critical to ensure that the PO is accurate and comprehensive to avoid misunderstandings or discrepancies.
Automate the generation of purchase orders through procurement software to ensure consistency and accuracy. Automation also allows for real-time tracking and updates on the status of each order.
-
Order and delivery management
The order management stage involves coordinating with the supplier to ensure that the goods or services are delivered as per the terms specified in the PO. This includes tracking the order status, managing delivery schedules, and resolving any issues that may arise during transportation. Effective order management helps maintain strong supplier relationships and ensures that production or operations are not disrupted.
Implement order tracking systems that provide real-time visibility into the supply chain. This enables quick responses to potential delays or issues, ensuring smooth and timely deliveries.
-
Invoice processing and payment
Once the goods or services are received, the supplier sends an invoice, which needs to be processed for payment. The procurement team conducts a three-way match, comparing the purchase order, delivery receipt, and invoice to ensure all details align. This process helps verify that the correct items were delivered, in the agreed quantities, and at the negotiated price. If everything matches, the invoice is approved for payment.
Use automated invoice processing systems that can streamline the matching process, flag discrepancies, and reduce the risk of errors. This improves efficiency and ensures timely payments, strengthening supplier relationships.
-
Record keeping and documentation
The final stage of the procurement process flow is record keeping. Maintaining comprehensive records of all procurement transactions is crucial for compliance, future audits, and financial reporting. Proper documentation also helps businesses analyze past purchases, assess supplier performance, and make informed decisions for future procurement activities.
Centralize all procurement data in a digital system that allows for easy retrieval, reporting, and analysis. This supports transparency, compliance, and strategic planning by providing insights into spending patterns and supplier reliability.
The benefits of a well-structured procurement process flow
A well-structured procurement process flow is not just about following a sequence of steps; it’s about creating a system that drives operational efficiency, cost control, and strategic value for an organization. When companies implement a robust procurement flow, they can reap numerous benefits that extend beyond the purchasing department, positively impacting the overall business. Below are some key advantages:
-
Improved cost control and savings
One of the most significant benefits of a structured procurement process is the ability to control costs effectively. By standardizing procedures for supplier selection, purchase requisitions, and order management, organizations can ensure that all purchases are made at the best possible price. This structured approach helps in negotiating better deals with suppliers, leveraging bulk discounts, and avoiding unnecessary expenditures.
Furthermore, a clear procurement process prevents unauthorized spending, also known as “maverick spending.” By requiring proper approvals at various stages, companies can enforce budget compliance and minimize unexpected costs. Organizations that implement e-procurement software solutions often find that automating the procurement flow leads to even greater savings by reducing the time and labor associated with manual purchasing tasks.
-
Enhanced supplier relationships
A streamlined procurement process flow fosters better communication and stronger relationships with suppliers. When suppliers have a clear understanding of an organization’s purchasing processes, they can better meet expectations related to quality, delivery, and cost. Consistent communication and timely payments strengthen trust, which can lead to long-term partnerships and more favorable contract terms.
Moreover, regular performance evaluations integrated into the procurement process help organizations identify reliable suppliers and address issues promptly. By building strong supplier networks, companies can secure reliable sources for critical goods and services, reducing the risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
-
Operational efficiency and time savings
Operational efficiency is a core benefit of a structured procurement process. Clear guidelines and standardized workflows minimize the confusion and delays that often accompany manual or ad-hoc purchasing processes. Automation plays a crucial role here; by using digital procurement platforms, organizations can automate repetitive tasks such as purchase order creation, invoice processing, and approvals. This not only speeds up the procurement cycle but also reduces the likelihood of errors.
With automated systems, procurement teams can shift their focus from transactional activities to more strategic tasks, such as supplier negotiations, market research, and process improvements. The time saved through efficiency gains also translates into quicker order fulfillment, ensuring that internal stakeholders receive the goods and services they need without delays.
-
Better compliance and risk management
Compliance with internal policies and external regulations is crucial for organizations, especially those operating in highly regulated industries. A structured procurement process flow helps ensure that all purchases are documented, approved, and compliant with legal requirements. This reduces the risk of non-compliance, which can lead to financial penalties and reputational damage.
Additionally, having a defined process in place makes it easier to conduct audits and maintain transparency. Companies can track every step of the procurement journey, from the initial requisition to the final payment, ensuring that all transactions are documented properly. This level of visibility also helps in managing risks, such as supply chain disruptions, by allowing procurement teams to respond quickly to issues as they arise.
-
Strategic insights through data analytics
A well-organized procurement process generates a wealth of data that can be analyzed to gain strategic insights. By centralizing procurement data, organizations can track spending patterns, supplier performance, and cost trends over time. This information can be used to make informed decisions, such as identifying areas where costs can be reduced or where supplier contracts should be renegotiated.
Advanced procurement software often includes analytics tools that can highlight inefficiencies, forecast demand, and suggest improvements. For instance, businesses can use data to identify trends in maverick spending, allowing them to address these issues and enforce better purchasing compliance. The ability to analyze and act on procurement data is essential for companies looking to optimize their operations and improve overall business performance.
Common challenges in managing procurement process flow
Even with a well-structured procurement process flow, organizations often face challenges that can disrupt efficiency, increase costs, and hinder effective procurement management. Understanding these common issues can help businesses proactively address and mitigate them, ensuring a smoother procurement experience. Below are some of the most prevalent challenges:
-
Fragmented supplier management
Managing a diverse supplier base can be difficult, especially for larger organizations that source products and services from multiple vendors across different categories. Fragmentation can lead to inconsistent service levels, difficulties in maintaining quality standards, and missed opportunities for bulk discounts and cost savings. When suppliers are not managed strategically, it becomes harder to track performance, address issues, and build long-term partnerships.
Implement a strategic sourcing approach that consolidates suppliers where possible. Building strong, long-term relationships with fewer, reliable suppliers can streamline procurement, enhance quality, and create opportunities for better pricing. Additionally, using supplier management software can centralize information, making it easier to track performance and maintain communication.
-
Lack of visibility and data integration
A major obstacle for many organizations is the lack of visibility into procurement activities. Without a centralized system to track purchases, requisitions, approvals, and payments, it’s difficult to monitor spending patterns, evaluate supplier performance, and identify areas of inefficiency. This lack of visibility often results in poor decision-making, delayed processes, and higher costs.
Digital procurement platforms can provide real-time visibility into the procurement process, from initial requisition to final payment. These systems enable businesses to track every transaction, ensuring transparency and easy access to data. Advanced analytics tools can also help identify spending patterns, inefficiencies, and potential cost-saving opportunities.
-
Maverick spending
Maverick spending occurs when employees make purchases outside of the established procurement process, often bypassing approval protocols. This can lead to budget overruns, inconsistent product quality, and missed opportunities for negotiated savings. Maverick spending is a symptom of a lack of control and visibility in the procurement process, and it can be costly for organizations that don’t address it effectively.
Enforce procurement policies strictly by implementing automated approval workflows that require all purchases to go through the designated channels. Training employees on the importance of compliance and the benefits of following the proper process can also help minimize maverick spending. Some companies use procurement cards (P-cards) or digital procurement systems to track and manage all purchases, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized spending.
-
Manual and inefficient processes
Despite advances in technology, many organizations still rely on manual processes for procurement tasks like purchase requisitions, approvals, order management, and invoice processing. Manual methods are time-consuming, prone to errors, and often result in process bottlenecks. For example, a manual purchase requisition process can lead to delays in approvals, which in turn delays order placement and disrupts supply chains.
Automation is key to overcoming inefficiencies in the procurement process. Digital procurement solutions can automate repetitive tasks, such as purchase order creation, invoice matching, and approval workflows. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces the risk of errors, ensuring that procurement activities are carried out accurately and efficiently.
-
Compliance and risk management
Procurement processes must adhere to both internal policies and external regulations. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, financial losses, and damage to the company’s reputation. Managing compliance is particularly challenging for organizations operating in multiple regions, each with its own regulatory requirements. Additionally, procurement often involves managing risks related to supplier reliability, market volatility, and contract enforcement.
Establish clear procurement policies that outline compliance requirements and ensure that all stakeholders are aware of them. Using procurement software that integrates compliance checks can help organizations adhere to regulations without added manual effort. Regular audits of procurement processes and contracts can further help in identifying and mitigating risks.
Best practices for optimizing procurement process flow
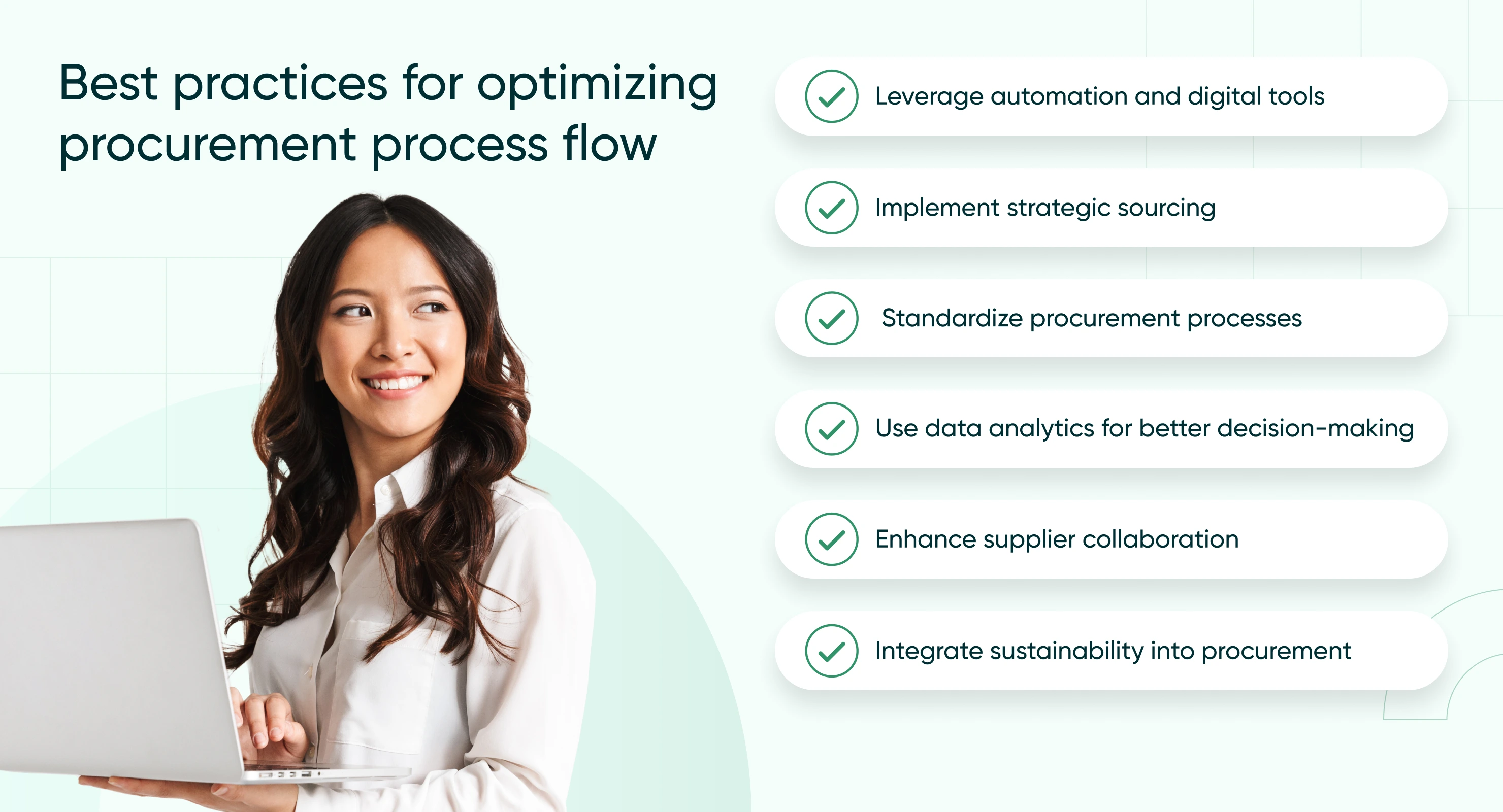
To get the most out of a procurement process, organizations should not only focus on following a structured workflow but also continuously seek to optimize their procedures. An optimized procurement process flow reduces costs, increases efficiency, and improves supplier relationships, ultimately driving greater strategic value. Here are some best practices for optimizing procurement:
-
Leverage automation and digital tools
One of the most effective ways to optimize procurement is through automation. Manual processes, such as purchase requisitions, approvals, and invoice processing, can be time-consuming and prone to errors. By automating these tasks, organizations can speed up the procurement cycle, reduce administrative costs, and minimize the risk of errors. Digital procurement platforms can also provide real-time tracking, automated purchase order creation, and streamlined invoice matching, leading to a smoother procurement process.
Invest in an e-procurement platform that integrates with your existing systems. This allows for better data sharing and streamlined workflows across departments. For example, automated approval workflows can significantly reduce the time needed for requisitions to pass through multiple levels of review.
-
Implement strategic sourcing
Strategic sourcing goes beyond simply finding the lowest-priced supplier. It involves evaluating suppliers based on a broader range of criteria, including quality, reliability, and long-term value. By analyzing spend categories and assessing supplier performance, organizations can identify the best suppliers to partner with for strategic purchases. This approach helps to build strong, long-term relationships with key suppliers, ensuring better terms, improved quality, and more reliable deliveries.
Regularly review supplier performance and renegotiate contracts where possible. Strategic sourcing can also help companies identify opportunities for bulk purchasing, which can lead to cost savings and more efficient procurement.
-
Standardize procurement processes
Consistency is key to efficiency. By standardizing procurement procedures across the organization, companies can ensure that all teams follow the same protocols, reducing the chances of errors and miscommunication. This standardization also helps in enforcing compliance with internal policies and external regulations, as every procurement activity follows a uniform approach.
Develop clear guidelines for each stage of the procurement process and ensure all relevant employees are trained on these standards. Having a standardized set of forms, templates, and workflows simplifies the process and reduces the learning curve for new staff members.
-
Use data analytics for better decision-making
Data is one of the most valuable assets in procurement. By analyzing procurement data, organizations can identify spending patterns, monitor supplier performance, and uncover inefficiencies in the process. Advanced data analytics tools can provide insights that help procurement teams make informed decisions, from choosing suppliers to deciding on order quantities. Data-driven procurement allows for better demand forecasting, cost management, and risk mitigation.
Utilize dashboards and reporting tools that provide real-time insights into procurement activities. Regularly reviewing this data helps in identifying trends, such as areas where maverick spending is occurring, or which suppliers consistently perform well. This allows for proactive management and continuous process improvement
-
Enhance supplier collaboration
Building strong relationships with suppliers is essential for a successful procurement process. Collaboration involves more than just placing orders; it requires clear communication, timely payments, and mutual understanding of goals. By engaging suppliers as partners, companies can negotiate better terms, ensure consistent quality, and even collaborate on product innovation. A collaborative approach can also help in managing supply chain risks by fostering trust and ensuring flexibility when facing disruptions.
Establish regular communication channels with key suppliers to discuss performance, future needs, and areas of improvement. Consider using supplier management software to track communications, agreements, and performance metrics, which can help strengthen these relationships over time.
-
Integrate sustainability into procurement
Modern procurement strategies increasingly emphasize sustainability, focusing on the environmental and social impacts of procurement decisions. Sustainable procurement practices involve sourcing from suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly and ethical practices, such as reducing waste, minimizing carbon footprints, and ensuring fair labor practices. Integrating sustainability into procurement can enhance brand reputation, ensure regulatory compliance, and contribute to broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
Develop a sustainability policy that outlines clear criteria for selecting suppliers based on their environmental and ethical practices. Consider certifications like ISO 14001 (environmental management) or Fair Trade standards as part of your supplier selection criteria. This not only ensures compliance but also appeals to customers who prioritize sustainability.
Visual aids: Creating an effective procurement process flowchart
A procurement process flowchart is a visual representation of the steps involved in procurement, from identifying needs to finalizing payment. It is an essential tool that helps simplify complex processes, enabling stakeholders to understand each phase and how they connect. A well-designed flowchart can be used to streamline operations, train new team members, and improve communication between departments by providing a clear visual guide to procurement activities. Below are guidelines and best practices for creating effective procurement process flowcharts:
-
Why use a procurement process flowchart?
Flowcharts offer a straightforward way to map out the procurement process, making it easier for everyone to understand how each stage fits into the larger workflow. By visualizing the process, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Flowcharts also serve as a training tool for new employees, providing a clear picture of the procurement steps and how they should be executed.
Moreover, having a visual guide can foster transparency. Teams can quickly reference the flowchart to understand where their tasks fit within the procurement process, ensuring everyone is aligned and understands their responsibilities. This transparency is particularly valuable for cross-functional teams that need to coordinate actions across departments.
-
Key elements of a procurement flowchart
A typical procurement process flowchart includes the following elements:
- Start point: The beginning of the process, usually marked by a need or request for goods/services.
- Decision points: Stages where approvals are needed or where choices must be made (e.g., selecting a supplier).
- Process steps: Tasks that need to be completed, such as creating a purchase requisition, issuing a purchase order, or processing an invoice.
- Connectors: Arrows or lines that show the flow of the process, guiding users through each step sequentially.
- End point: The conclusion of the procurement process, which is typically marked by the final payment or record-keeping.
Use consistent symbols and colors throughout the flowchart to make it easier to read and follow. For example, use diamonds for decision points, rectangles for tasks, and arrows to show direction.
-
Steps to create an effective procurement flowchart
Creating a clear and useful procurement flowchart involves careful planning and attention to detail. Here’s how you can design an effective flowchart:
- Map out the procurement steps: List out each stage of your procurement process, including every decision point and task. Ensure that the steps are organized logically from start to finish. Start with identifying the need, move through supplier selection, and end with payment and record-keeping.
- Define key roles and responsibilities: Include information on which departments or individuals are responsible for each task. This ensures accountability and helps clarify who should take action at each step.
- Incorporate automation points: Highlight where automation is used (or could be used) to streamline the process. For example, automated approval workflows can be indicated to show where digital tools help reduce manual efforts.
- Design for clarity: Keep the design simple and easy to understand. Avoid clutter by focusing on essential information. Ensure that the flowchart is accessible and that any stakeholders can quickly grasp the flow of activities without needing extensive explanations.
- Test and update regularly: Once your flowchart is designed, share it with team members for feedback. Make sure it accurately represents the actual workflow, and update it as processes change. Regular reviews ensure that the flowchart remains relevant and reflects any new improvements to the procurement process.
-
Examples of procurement flowcharts
- Basic procurement flowchart: Includes the essential steps from need identification to payment, providing a straightforward visual for organizations with simpler procurement needs.
- Detailed flowchart for complex organizations: Includes additional elements like supplier evaluations, contract management, and compliance checks. This type of chart is more comprehensive and can accommodate multiple layers of decision-making and approvals.
- Automated procurement flowchart: Shows how digital procurement platforms integrate into the process, highlighting where automation reduces manual tasks. It can also illustrate data flows and integrations with other business systems, like ERP software.
Consider creating multiple versions of your flowchart depending on the audience. A high-level version for executives may focus on the main stages, while a detailed version for the procurement team can include more granular tasks and decision points.
So what?
Mastering the procurement process flow is complex and ever-evolving as companies need to constantly evaluate and adapt to achieve peak purchasing efficiency.
Ultimately, the procurement process flow is not just a set of steps but a strategic framework that can drive organizational success. By continually optimizing this process and leveraging modern technology, companies can ensure they remain competitive, agile, and ready to meet the demands of an ever-evolving business environment. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, investing in a robust procurement process is a strategic move that will yield long-term benefits, from cost savings to improved supplier performance and beyond.

2025 Spend Management Software Buyer’s Guide
Choose the spend management solution best suited to your organization’s needs with an overview of the 2025 software ecosystem, feature comparisons, and a free vendor capability evaluation checklist.
