Purchase Order Process Flow: From Creation to Payment
Every dollar matters when it relates to your company’s bottom line.
Whether you are reporting to your board, trying to streamline your company spending, or aiming to maximize the margins on your products, being able to quantify and account for every dollar coming out is a top priority for finance teams.
One area within an organization that has significant saving potential is procurement. Businesses can save up to 30% on procurement costs by optimizing their purchase order processes. That amount is no small drop in the bucket.
Crafting a streamlined purchase order (PO) process is essential for efficient business operations, ensuring that all transactions are accurately documented and managed. In this article, we’ll walk you through the purchase order process flow, from creation to payment, helping you understand each step and its overall importance to your procurement strategy.
Understanding the purchase order process
What is a purchase order?
A purchase order (PO) is a document issued by a buyer to a supplier, indicating types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services. It’s a formal request to purchase, serving as a contract once accepted by the supplier. The PO outlines the specifics of the purchase, ensuring both parties have a clear understanding of what is being ordered, the terms of the agreement, and the payment conditions.
Importance of a structured purchase order process
Having a well-defined purchase order process brings numerous benefits, such as improved accuracy in transactions, better supplier relationships, and significant cost savings. It ensures that all purchases are authorized, budgeted, and traceable. A structured PO process helps prevent fraud, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with internal policies and external regulations.

Ready to streamline your purchase order process?
Discover how our purchase order software can help you gain control over your procurement, save time, and maximize cost efficiency. See it in action by requesting a demo today!
Step-by-step purchase order process flow
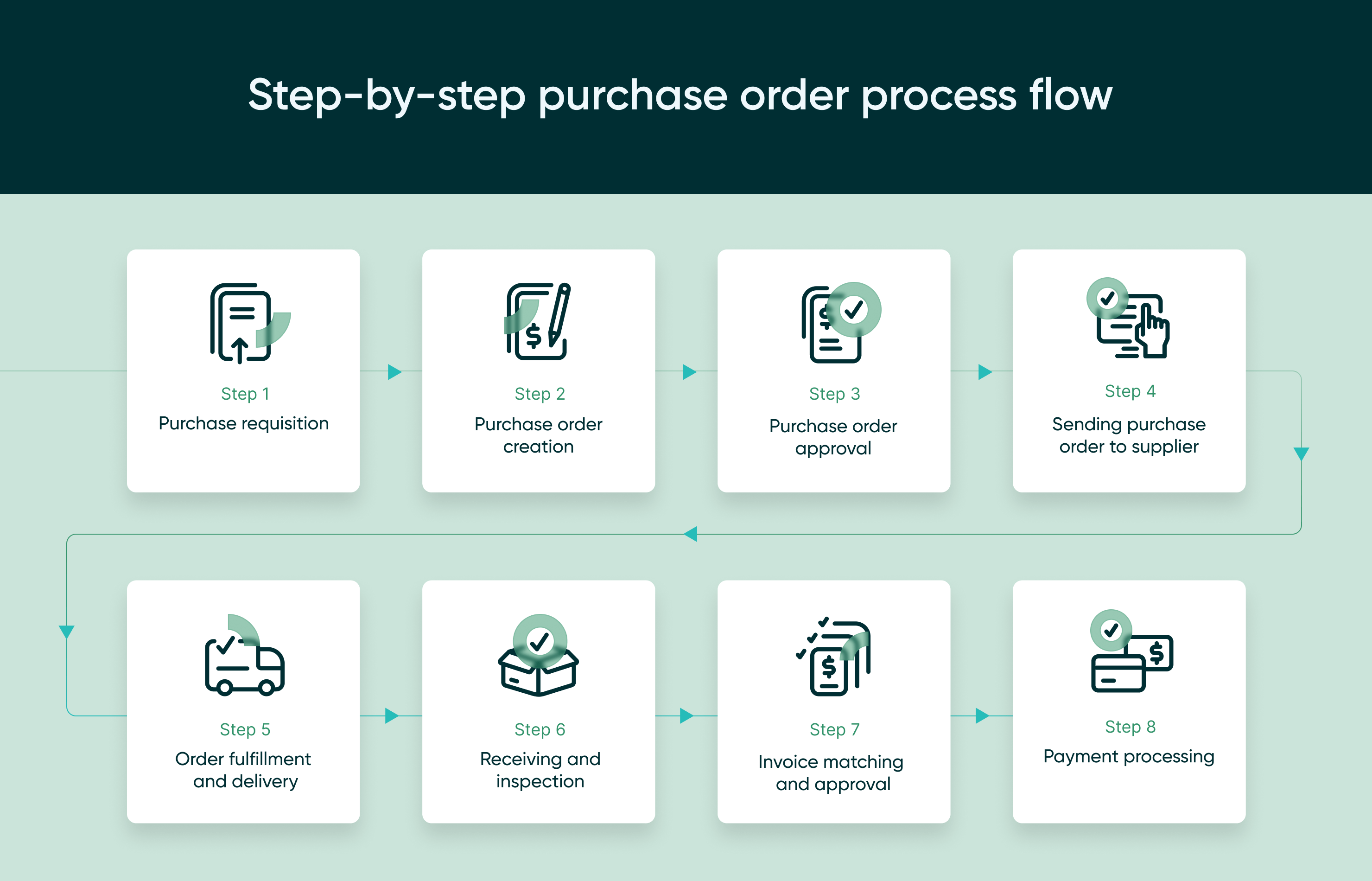
Step 1: Purchase requisition
The purchase requisition is an internal document created by a department requesting the procurement of goods or services. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for the entire purchase order process.
Purchase requisition starts with authorization. The purchase requisition must be approved by relevant authorities within the organization, ensuring that the purchase is necessary and that funds are available. During the need assessment stage, the department requesting the purchase needs to justify why the items or services are needed. This involves evaluating current inventory levels, upcoming projects, and business requirements. And finally, you will need requisition forms, which are detailed forms specifying the required items are filled out. These forms include information such as item descriptions, quantities, preferred suppliers, and expected costs.
Step 2: Purchase order creation
Once the requisition is approved, a purchase order is created. This document includes:
-
PO templates: Standardized templates ensure consistency across all purchase orders. These templates typically include fields for all necessary information, reducing the chance of missing details.
-
Essential elements: A complete purchase order includes a PO number, date, supplier details, item descriptions, quantities, prices, and terms. Including all these elements ensures clarity and prevents disputes.
Step 3: Purchase order approval
Before sending the PO to the supplier, it undergoes an approval process. This step adds a layer of oversight to ensure the accuracy and appropriateness of the order. For multi-level approvals, different levels of management review and approve the PO. This might involve department heads, finance managers, and procurement officers, depending on the organization’s structure and the purchase’s value.
Another PO approval method is through automated approval systems. Many organizations use software to streamline and track approvals. These systems can automatically route POs to the appropriate approvers and maintain a record of the approval process.
Step 4: Sending purchase order to supplier
After approval, the PO is sent to the supplier through various methods:
-
Email, EDI, procurement software: Ensuring the PO reaches the supplier promptly is crucial. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and procurement software can automate this process, reducing delays and errors.
-
Tracking delivery: Monitoring the dispatch and receipt of the PO is important to ensure timely processing. This can be done using tracking numbers and receipt confirmations.
-
Supplier confirmation: The supplier acknowledges and confirms the PO. This confirmation ensures that the supplier has received the order and agrees to the terms outlined.
Step 5: Order fulfillment and delivery
The supplier fulfills the order by delivering the goods or services as specified in the PO. This step involves delivery schedules, timely delivery in accordance with agreed terms is crucial. The supplier must adhere to the delivery dates specified in the PO to avoid disrupting the buyer’s operations. And this step also includes receiving goods, where the buyer receives and checks the delivery. This involves inspecting the items to ensure they match the specifications in the PO.
Step 6: Receiving and inspection
Upon receiving the goods, they are inspected to ensure they meet the specifications outlined in the PO:
-
Verifying quantities and quality: Ensuring the delivered items match the PO in terms of quantity and quality is essential. This involves counting items and checking for any damage or defects.
-
Documenting discrepancies: Any discrepancies between the PO and the delivered goods must be documented and addressed. This might involve contacting the supplier to resolve issues or arranging for returns or replacements.
-
Updating inventory: Adding received items to inventory records ensures that inventory levels are accurate. This is important for maintaining stock levels and planning future purchases.
Step 7: Invoice matching and approval
This step involves the three-way matching process to ensure accuracy before payment. It is a critical control mechanism to prevent overpayments and fraud. The three-way matching process compares the PO, receiving report, and supplier invoice. All three documents must match in terms of quantities, prices, and terms before payment is authorized.
You must also handle discrepancies. This involves resolving any mismatches is important to ensure accurate payments. Handling discrepancies might also involve contacting the supplier for clarification or issuing a debit note for overcharges. Leveraging automated matching systems involves using software to streamline this process and can significantly reduce errors and speed up the approval process. Automated systems can flag discrepancies and route them for review.
Step 8: Payment processing
Finally, the payment to the supplier is processed. This step ensures that suppliers are paid accurately and on time. Adhering to agreed payment terms is important for maintaining good supplier relationships. Payment terms might include net 30, net 60, or other arrangements. Common payment methods include checks, wire transfers, or electronic payments. The method chosen can depend on the supplier’s preferences and the buyer’s policies.
Recording the transaction means documenting the payment in the accounting system, ensuring that financial records are accurate and up-to-date. This is important for budgeting and financial reporting.
Best practices for an efficient purchase order process
Automation and technology
Leveraging procurement software can significantly streamline the purchase order process, reducing manual errors and saving time. Automation can handle repetitive tasks, such as generating POs and routing them for approval, freeing up staff to focus on more strategic activities.
Standardization and templates
Using standardized forms and templates ensures consistency and efficiency across all purchase orders. Templates can include all necessary fields, reducing the chance of missing important information. Standardization also makes it easier to train staff and implement process improvements.
Regular audits and reviews
Conducting regular audits helps maintain compliance and identifies areas for process improvement. Audits can uncover issues such as unauthorized purchases, discrepancies between POs and invoices, and delays in the approval process. Addressing these issues can lead to significant cost savings and process efficiencies.
Training and communication
Ensuring that staff are well-trained and maintaining clear communication channels with suppliers can prevent misunderstandings and errors. Training should cover the entire purchase order process, from requisition to payment, and emphasize the importance of accuracy and compliance. Clear communication with suppliers helps ensure that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the purchase order process
Conclusion
Strategic procurement often leads to more intentional spending practices.
More specifically, a well-structured purchase order process creates opportunities to make your overall business operations strategy more efficient.
By following the end-to-end steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure your transactions are accurate, timely, and well-documented. Modernizing your current PO processes with the right procure-to-pay software will not only improve your supplier relationships and spend visibility, but you will also be able to accurately quantify your savings.

Webinar: 5 Strategies for Cost Reduction and Value Creation
Learn how best-in-class procurement leaders are leveraging the right technology to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve the effectiveness of their purchasing.
