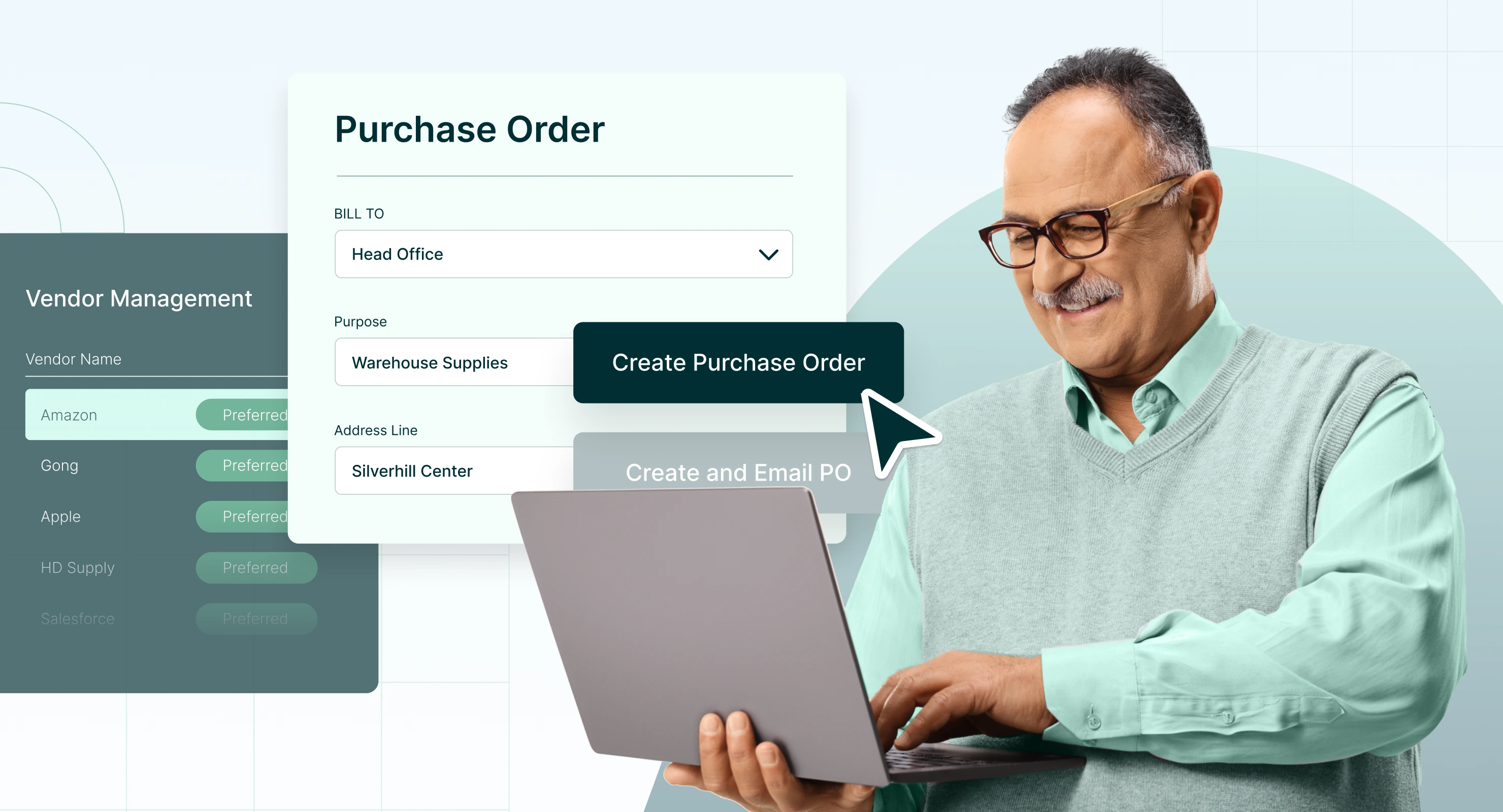
Purchasing problems and solutions: 10 common challenges
Navigating challenges that arise during the purchasing process is a critical task for organizations striving for operational excellence and competitive advantage. From managing complex supplier relationships and ensuring compliance with regulations, to optimizing procurement workflows and leveraging technology for efficiency gains, the procurement landscape is fraught with challenges that demand strategic attention and innovative solutions.
The role of procurement has evolved significantly, moving beyond mere transactional activities to become a strategic function that contributes directly to an organization’s bottom line and long-term success. In this context, identifying common procurement challenges and implementing effective solutions becomes paramount for businesses aiming to enhance their procurement operations, minimize risks, and maximize value from their supply chains.
This article delves into “Purchasing Problems and Solutions: 10 Common Challenges,” offering insights into the critical issues faced by procurement professionals and outlining strategies to address these challenges. From risk management and lack of visibility to choosing the right vendors and optimizing the purchasing process, we explore how organizations can navigate these complexities to achieve procurement excellence.
Moreover, we highlight the pivotal role of technology, particularly procurement software, in transforming procurement practices. Through automation, real-time data analytics, and enhanced supplier collaboration, procurement software emerges as a key enabler in solving many of the challenges discussed. As businesses continue to adapt to a rapidly changing economic environment, embracing digital transformation in procurement is not just an option—it’s a necessity.
Join us as we examine each of these ten common procurement challenges in detail, providing actionable solutions and showcasing how organizations can leverage technology to streamline their procurement processes, mitigate risks, and build stronger, more resilient supply chains. Whether you’re a seasoned procurement professional or new to the field, this exploration offers valuable perspectives on enhancing procurement efficiency and effectiveness in today’s complex business landscape.
1. Risk management and mitigation in procurement
Introduction to Risk Management in Procurement
Risk management and mitigation form the cornerstone of effective procurement processes. In the complex and interconnected world of supply chain operations, the ability to proactively identify, assess, and address potential risks is not just advantageous—it is essential. Effective risk management ensures business continuity, safeguards against financial losses, and upholds the integrity of supply chains, even in the face of unforeseen challenges.
The Significance of Risk Management
At its core, risk management in procurement is about foreseeing potential issues that could disrupt the supply chain, affect the quality of goods and services, or impact the financial stability of an organization. This includes everything from supplier insolvency, geopolitical issues affecting supply chain routes, to quality control problems. By addressing these risks head-on, organizations can avoid costly disruptions, maintain operational efficiency, and protect their brand reputation.
Strategies for Risk Identification and Assessment
The first step in a robust risk management strategy is the identification and assessment of potential risks. This involves a comprehensive analysis of the procurement process to pinpoint vulnerabilities. Key strategies include:
- Supplier Evaluation: Conducting thorough assessments of suppliers’ financial stability, quality control measures, and delivery reliability.
- Market Analysis: Staying informed about global market trends, including geopolitical issues, commodity price fluctuations, and regulatory changes that could impact supply chains.
- Contract Analysis: Reviewing procurement contracts for clauses that might pose risks under certain conditions, such as penalties for late deliveries or provisions for force majeure.
Mitigating Procurement Risks
Once risks are identified and assessed, the next step is mitigation. Effective strategies include:
- Diversifying Suppliers: Reducing dependency on a single supplier by diversifying sources can mitigate risks associated with supplier failure.
- Strategic Stocking: Maintaining strategic stock levels for critical items to buffer against supply chain disruptions.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conducting regular audits of suppliers and internal processes to ensure compliance with quality and delivery standards.
The Role of Procurement Software in Risk Management
In today’s digital age, procurement software plays a pivotal role in enhancing risk management strategies. These tools offer several features that aid in the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks:
- Supplier Management Features: Procurement software often includes comprehensive supplier management modules that help in tracking and evaluating supplier performance, financial stability, and compliance with contracts.
- Risk Analysis Tools: Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities enable organizations to perform detailed risk analyses, identifying potential issues before they become problems.
- Automated Alerts: Many procurement softwares feature automated alerts that notify procurement teams of potential risks, such as price fluctuations or delivery delays, allowing for swift action.
Conclusion
The integration of risk management and mitigation strategies in procurement is not just about avoiding negative outcomes; it’s a strategic approach that drives operational efficiency, financial stability, and competitive advantage. Through diligent risk identification, thorough assessment, strategic mitigation, and the leveraging of cutting-edge procurement software, organizations can build resilient supply chains capable of weathering any storm. This proactive approach not only safeguards operations but also supports sustainable growth in an ever-evolving global market.
2. Lack of visibility in procurement processes
The Challenge of Invisibility
In the intricate dance of procurement, visibility—or the lack thereof—can significantly dictate the rhythm of an organization’s operations. A lack of visibility in procurement processes often leads to several profound issues, including inefficient spend management, delayed deliveries, and compromised supplier relationships. Without a clear view of procurement operations, organizations might find themselves navigating through a fog of uncertainty, making decisions based on incomplete or outdated information.
Consequences of Reduced Visibility
The implications of reduced visibility in procurement are far-reaching. Organizations may encounter:
- Inefficient Spend Management: Without clear insights into spending patterns, organizations can miss opportunities for bulk purchasing, fail to leverage supplier discounts, and inadvertently allow maverick spending to occur.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: A lack of visibility into supplier operations and inventory levels can lead to unexpected supply chain disruptions, impacting production schedules and market delivery.
- Compliance Risks: Without comprehensive oversight, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and contractual obligations becomes more challenging, potentially leading to legal and financial repercussions.
Achieving Enhanced Transparency
Enhancing transparency in procurement processes is pivotal to overcoming these challenges. This can be achieved through:
- Centralized Procurement Data: Consolidating procurement data into a single, accessible platform ensures that decision-makers have a holistic view of procurement operations.
- Collaborative Supplier Relationships: Building strong, transparent relationships with suppliers enables better communication and collaboration, facilitating smoother operations and problem resolution.
- Process Standardization: Standardizing procurement processes across all departments ensures consistency and makes it easier to track and manage procurement activities.
The Role of Procurement Software
Procurement software emerges as a beacon of hope in the quest for enhanced visibility. These digital platforms are designed to provide real-time insights and data, enabling better decision-making throughout the procurement process. Key benefits include:
- Real-Time Data Access: Procurement software offers immediate access to critical data, such as spending patterns, supplier performance metrics, and inventory levels, allowing for timely and informed decisions.
- Automated Reporting: Automated, customizable reports generated by procurement software provide a clear overview of procurement activities, identifying areas for improvement and highlighting successes.
- Supplier Performance Tracking: Advanced features in procurement software allow for the monitoring of supplier performance against predefined metrics, ensuring that suppliers meet contractual obligations and performance standards.
Conclusion
The path to overcoming the challenges posed by a lack of visibility in procurement lies in the adoption of strategies and tools that enhance transparency. By centralizing data, fostering collaborative supplier relationships, standardizing processes, and leveraging the capabilities of procurement software, organizations can gain the insights needed for effective decision-making. This not only streamlines procurement operations but also positions organizations for stronger, more resilient supply chains and a competitive advantage in the marketplace. The clarity provided by enhanced visibility is not just a luxury; it’s a strategic necessity in the modern business landscape.
3. Collecting accurate data and insights
The Foundation of Effective Procurement
At the heart of any successful procurement strategy lies a foundation built on accurate data and insightful analysis. The ability to collect, analyze, and act upon precise data not only optimizes procurement operations but also drives strategic decision-making that aligns with organizational goals. In the era of information, data serves as the compass that guides procurement professionals through the complexities of market dynamics, supplier performance, and spending efficiencies.
The Importance of Accurate Data
Accurate data and insights in procurement serve several critical functions:
- Strategic Sourcing: They enable procurement teams to identify the best suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and secure high-quality goods and services at optimal prices.
- Spend Analysis: They provide visibility into organizational spending patterns, highlighting opportunities for cost savings and budget optimization.
- Risk Management: Accurate data helps in identifying potential risks in the supply chain, enabling proactive measures to mitigate these risks.
- Compliance Monitoring: They ensure that procurement activities adhere to internal policies and external regulations, reducing the risk of financial penalties and reputational damage.
Methods for Data Collection and Analysis
Collecting and analyzing data in procurement involves a systematic approach to gather relevant information and derive actionable insights. Key methods include:
- Supplier Assessments: Conducting thorough evaluations of suppliers’ capabilities, financial stability, and compliance with quality standards to ensure they meet organizational needs.
- Market Research: Keeping abreast of market trends, price fluctuations, and technological advancements to inform procurement strategies.
- Performance Metrics: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) related to procurement activities, such as order accuracy, delivery times, and cost savings, to assess efficiency and effectiveness.
Streamlining Data Collection with Procurement Software
Procurement software stands out as a transformative tool in the collection and analysis of procurement data. These digital solutions streamline data-related activities through:
- Centralized Data Repository: Procurement software creates a unified platform where all procurement-related data is stored, making it easily accessible for analysis and reporting.
- Automated Data Collection: By automating the data collection process, procurement software ensures that data is up-to-date and accurate, minimizing the risk of human error.
- Advanced Analytics: With built-in analytics capabilities, procurement software enables the analysis of complex data sets to uncover trends, identify savings opportunities, and inform procurement decisions.
- Customizable Dashboards: These platforms offer customizable dashboards that provide at-a-glance insights into procurement metrics, facilitating quick and informed decision-making.
Conclusion
The critical role of collecting accurate data and insights in procurement cannot be overstated. By harnessing the power of data, organizations can navigate the procurement landscape with confidence, making decisions that are informed, strategic, and aligned with their operational goals. The adoption of procurement software further enhances this capability, offering tools that streamline data collection and analysis, thus empowering procurement professionals to unlock the full potential of their procurement strategies. As organizations continue to embrace the digital transformation of procurement, the emphasis on accurate data and insights will remain a key driver of success in this dynamic function.
4. Implementing digital technologies for procurement
The Digital Gap in Traditional Procurement
In the age of digital transformation, procurement departments that lag in adopting digital technologies face significant challenges. Traditional, manual procurement processes are not only time-consuming but also prone to errors and inefficiencies. The absence of digital tools in procurement can lead to:
- Delayed Procurement Cycles: Manual processes slow down operations, from requisition to payment, affecting the organization’s ability to respond to market changes swiftly.
- Data Inaccuracy: Reliance on paper-based processes and spreadsheets increases the risk of data errors, impacting decision-making.
- Limited Visibility: Without digital solutions, gaining a comprehensive view of procurement activities, spending patterns, and supplier performance is challenging, leading to suboptimal strategic decisions.
- Decreased Collaboration: Manual processes hinder effective communication and collaboration among procurement teams, suppliers, and stakeholders.
The Path to Digital Transformation
The transition to digital procurement is not merely a trend but a strategic imperative. Digital transformation in procurement encompasses the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of procurement processes to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve outcomes. Key benefits include:
- Streamlined Processes: Digital tools automate repetitive tasks, freeing up procurement professionals to focus on strategic activities and decision-making.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Digital solutions offer sophisticated data management capabilities, ensuring accurate, real-time data is available for analysis.
- Increased Transparency: Digital technologies provide visibility into the entire procurement process, from sourcing to payment, enabling better control and management of procurement activities.
- Improved Supplier Relationships: Digital platforms facilitate better communication and collaboration with suppliers, leading to more effective partnerships and improved supplier performance.
Leveraging Procurement Software and Digital Tools
Procurement software and digital tools are at the forefront of the digital transformation in procurement, offering a multitude of functionalities that drive efficiency and outcomes:
- Electronic Procurement (e-Procurement) Systems: These systems digitize the end-to-end procurement process, from electronic tendering and e-auctioning to electronic purchase order processing and e-invoicing, significantly reducing cycle times and increasing process efficiency.
- Supplier Management Platforms: Digital platforms provide tools for better supplier management, including performance tracking, risk management, and collaborative planning, enhancing supplier relationships and ensuring compliance.
- Spend Analysis Tools: Advanced analytics tools enable procurement teams to analyze spending data deeply, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions.
- Contract Management Solutions: Digital contract management tools streamline contract creation, execution, and analysis for maximum operational and financial performance while reducing risks associated with non-compliance.
Conclusion
The adoption of digital technologies in procurement is essential for organizations seeking to overcome the limitations of traditional procurement processes. Digital transformation not only addresses these challenges but also unlocks new opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and strategic value creation. Through the strategic implementation of procurement software and digital tools, organizations can achieve a more agile, transparent, and effective procurement function, positioning themselves for success in a rapidly evolving business environment. As procurement continues to evolve, the embrace of digital technologies will undoubtedly be a defining factor in the competitiveness and resilience of organizations worldwide.
5. Building rapport with key stakeholders
The Essence of Stakeholder Relationships in Procurement
In the multifaceted realm of procurement, forging strong relationships with both suppliers and internal stakeholders is paramount. These relationships are the backbone of effective procurement operations, influencing everything from negotiation success to the seamless execution of procurement strategies. The significance of building rapport cannot be overstated—it enhances trust, encourages collaboration, and fosters a culture of mutual success.
Impact on Procurement Success
Strong stakeholder relationships contribute to procurement success in several key ways:
- Improved Negotiation Outcomes: Good relationships with suppliers open the door to better negotiation terms, which can lead to cost savings and improved service levels.
- Enhanced Supplier Performance: When suppliers are engaged as strategic partners, they are more likely to prioritize your needs, leading to better quality, innovation, and reliability.
- Increased Internal Alignment: Building rapport with internal stakeholders ensures procurement strategies align with organizational goals, facilitating smoother implementation and higher acceptance rates.
Strategies for Effective Communication and Collaboration
Building and maintaining strong relationships require deliberate strategies focused on effective communication and collaboration:
- Regular Communication: Establish regular touchpoints with suppliers and internal stakeholders to share updates, discuss challenges, and solicit feedback. This ongoing dialogue fosters transparency and trust.
- Joint Planning and Review Sessions: Involve key suppliers and stakeholders in planning and review sessions to align objectives, set performance metrics, and evaluate progress. This collaborative approach ensures all parties are working towards common goals.
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Implement clear mechanisms for resolving disputes or disagreements. Addressing issues promptly and fairly can prevent minor misunderstandings from escalating into major conflicts.
- Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledge and reward excellent performance, both from suppliers and internal stakeholders. Recognition can take many forms, from formal awards to public acknowledgment in meetings.
The Role of Technology in Facilitating Relationship Building
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing relationships with suppliers and internal stakeholders by facilitating communication, collaboration, and data sharing:
- Procurement Platforms: Centralized procurement platforms enable easy information sharing, order tracking, and performance monitoring, making it simpler for suppliers and procurement teams to collaborate efficiently.
- Collaborative Tools: Tools like video conferencing, instant messaging, and project management software can help maintain regular communication and collaboration with stakeholders, regardless of geographical location.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Advanced analytics tools provide insights into supplier performance, spending patterns, and market trends, enabling data-driven discussions and strategic decisions.
- Supplier Portals: Online portals offer suppliers direct access to relevant information, including order statuses, payment schedules, and performance feedback, fostering transparency and efficiency.
Conclusion
The ability to build and maintain strong relationships with suppliers and internal stakeholders is a critical component of procurement success. Through effective communication, collaboration, and the strategic use of technology, procurement professionals can cultivate these relationships, unlocking numerous benefits such as improved negotiations, enhanced supplier performance, and increased internal alignment. As the procurement landscape continues to evolve, the emphasis on building rapport with key stakeholders will remain a vital strategy for achieving operational excellence and strategic objectives.
6. Implementing compliance in procurement
Navigating the Compliance Landscape
In the intricate world of procurement, navigating the maze of regulations, standards, and contractual obligations presents a formidable challenge. Compliance is not merely a legal requirement; it’s a cornerstone of ethical and responsible procurement practices. Ensuring compliance safeguards organizations against legal penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses, reinforcing trust with clients, suppliers, and stakeholders.
The Critical Nature of Compliance
Compliance in procurement encompasses a broad spectrum, from adhering to international trade laws and environmental regulations to meeting industry-specific standards and contractual terms. The implications of non-compliance are significant, including hefty fines, legal battles, and a tarnished brand image. Beyond these repercussions, compliance ensures that procurement operations contribute positively to organizational integrity and sustainable business practices.
Challenges in Maintaining Compliance
Maintaining compliance poses several challenges, particularly for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions or sectors. These challenges include:
- Complex Regulatory Environments: Keeping abreast of evolving regulations and standards across different regions and industries can be daunting.
- Data Management and Visibility: Ensuring accurate documentation and visibility of compliance-related data throughout the procurement process is critical but challenging in the absence of robust systems.
- Supplier Compliance: Extending compliance requirements to suppliers and ensuring their adherence complicates the procurement process, requiring diligent management and monitoring.
Procurement Software as a Compliance Ally
Procurement software emerges as a powerful ally in the quest for compliance, offering features and functionalities designed to simplify regulatory adherence:
- Automated Compliance Checks: Procurement software can automate the process of checking and ensuring compliance with various regulations and standards, significantly reducing the risk of human error.
- Centralized Documentation: These platforms provide a centralized repository for all compliance-related documents, making it easier to manage, access, and audit procurement data.
- Supplier Management: Advanced supplier management features enable businesses to assess and monitor suppliers’ compliance status, ensuring that all partners meet the required standards and regulations.
- Real-Time Updates and Alerts: Procurement software can offer real-time updates on regulatory changes and send alerts about potential compliance issues, allowing organizations to respond swiftly and adjust their practices accordingly.
Conclusion
The challenge of implementing compliance in procurement is multifaceted, involving the management of complex regulatory environments, data visibility, and supplier adherence. However, the importance of compliance extends beyond legal adherence; it’s about fostering ethical, sustainable, and socially responsible procurement practices. With the aid of procurement software, businesses can navigate the compliance landscape more effortlessly, ensuring that their procurement operations uphold the highest standards of integrity and contribute to the organization’s long-term success. Embracing digital tools in procurement not only mitigates the risk of non-compliance but also positions organizations as leaders in ethical and responsible business practices.
7. Creating or using contracts
Understanding Contract Management Complexities
Contract management is a critical aspect of the procurement process, involving the creation, negotiation, execution, and monitoring of contracts with suppliers. It serves as the legal foundation for the procurement of goods and services, outlining terms, conditions, and expectations between parties. Despite its importance, contract management is fraught with complexities that can lead to inefficiencies, misunderstandings, and potential disputes. These challenges stem from the need to ensure contracts are fair, transparent, and aligned with organizational objectives while also complying with applicable laws and regulations.
The Intricacies of Contract Management
Several factors contribute to the complexities of contract management in procurement:
- Legal Compliance: Contracts must comply with local, national, and international laws, requiring up-to-date legal knowledge and expertise.
- Negotiation Dynamics: The negotiation process can be intricate, with both parties seeking to protect their interests while forging a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Version Control: Managing multiple versions of contract documents during negotiations and ensuring all parties work from the most current version can be challenging.
- Performance Monitoring: Once executed, contracts must be actively monitored to ensure all parties fulfill their obligations, necessitating robust tracking mechanisms.
Best Practices for Contract Management
Adopting best practices in contract management can mitigate these challenges, enhancing efficiency and outcomes:
- Standardize Contract Templates: Develop standardized templates for common contract types to streamline creation and ensure consistency across agreements.
- Clear and Concise Language: Use clear, straightforward language to avoid ambiguity, making it easier for all parties to understand contract terms and obligations.
- Regular Reviews and Updates: Periodically review and update contracts to reflect changes in laws, regulations, and organizational policies.
- Establish Performance Indicators: Include specific performance indicators and milestones in contracts to facilitate monitoring and ensure accountability.
- Document Management: Implement a system for secure, organized document management, ensuring that all contract-related documents are easily accessible.
Enhancing Contract Management with Procurement Systems
Procurement systems play a pivotal role in automating and enhancing contract management processes:
- Automation of Contract Creation: Procurement software can automate the creation of contracts using standardized templates, reducing the time and effort involved in drafting documents.
- Digital Negotiation Tools: Some systems offer digital negotiation capabilities, enabling secure, real-time collaboration and version control, simplifying the negotiation process.
- Electronic Signatures: The use of electronic signatures allows for faster execution of contracts, eliminating the delays associated with traditional signing methods.
- Contract Repository: A centralized contract repository within procurement softwares ensures that all contract documents are securely stored and easily retrievable.
- Performance Tracking: Advanced procurement softwares include features for tracking contract performance against defined indicators, alerting procurement teams to potential issues or deviations.
Conclusion
Contract management is a complex yet crucial component of procurement, requiring careful attention to legal, negotiation, and performance monitoring aspects. By adhering to best practices and leveraging the capabilities of procurement systems, organizations can overcome the challenges of contract management, ensuring that contracts are not only effective and compliant but also serve as tools for achieving strategic procurement objectives. The integration of technology into contract management processes offers significant advantages, streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and ultimately contributing to the overall success of procurement activities.
8. Optimizing the purchasing process
Analyzing the Purchasing Process
The purchasing process in procurement, from requisition to payment, is fundamental to securing the goods and services that organizations require to operate. However, this process can often be fraught with inefficiencies that not only slow down operations but also lead to increased costs and reduced effectiveness. Common inefficiencies include manual data entry, lack of integration between procurement and finance systems, slow approval workflows, and inadequate supplier management.
Common Inefficiencies
- Manual Processes: Reliance on manual processes for requisition, approval, and order placement is time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Fragmented Systems: Disparate systems for procurement, inventory management, and accounting can lead to data silos, making it difficult to track spending and manage budgets effectively.
- Lengthy Approval Cycles: Complex or unclear approval hierarchies can significantly delay the procurement process, affecting the timely acquisition of necessary goods and services.
- Inadequate Supplier Integration: Limited communication and data exchange with suppliers can lead to inefficiencies in order placement, tracking, and receiving.
Streamlining the Purchasing Process
Optimizing the purchasing process requires a strategic approach focused on eliminating inefficiencies and enhancing agility. Key methods to streamline this process include:
- Automate Routine Tasks: Implement automation for routine tasks such as requisition, purchase order creation, and invoice processing to reduce manual workloads and improve accuracy.
- Integrate Procurement Systems: Ensure that procurement softwares are integrated with finance and inventory management systems for seamless data flow and comprehensive visibility.
- Simplify Approval Workflows: Streamline approval workflows to minimize steps and clarify approval authority, speeding up the purchasing process.
- Enhance Supplier Collaboration: Utilize platforms that enable direct communication and data exchange with suppliers for more efficient order management and fulfillment.
The Role of Procure-to-Pay Software
Procure-to-pay (P2P) software is designed to automate and integrate all phases of the procurement process, from the initial requisition to the final payment, offering a comprehensive solution to optimize purchasing. Key features and benefits include:
- Centralized Requisitioning: P2P software provides a centralized platform for requisitioning, allowing for easy creation, submission, and tracking of requisitions.
- Automated Approvals: By automating approval workflows, P2P systems ensure that requisitions and purchase orders are processed swiftly, adhering to predefined rules and thresholds.
- Seamless Integration: Integration with inventory and financial systems allows for real-time budget tracking and spend analysis, ensuring financial controls are maintained.
- Supplier Management: Advanced P2P solutions include supplier management features, facilitating better communication, order tracking, and performance analysis.
- Electronic Invoicing and Payment: The software streamlines the invoicing and payment process, reducing paperwork, speeding up transactions, and improving supplier relationships through timely payments.
Conclusion
Optimizing the purchasing process in procurement is essential for achieving operational excellence. By identifying and addressing common inefficiencies, organizations can enhance the efficiency, speed, and accuracy of their procurement activities. The adoption of procure-to-pay software plays a critical role in this optimization, offering tools and features that automate processes, integrate systems, and improve supplier collaboration. Through strategic improvements and technological advancements, procurement teams can transform the purchasing process into a streamlined, efficient operation that supports organizational goals and drives business success.
9. Issues with deliveries
Understanding Delivery Issues in Procurement
Delivery issues are a common challenge in procurement that can significantly disrupt the supply chain and affect business operations. These issues may range from delayed deliveries and damaged goods to incorrect orders, all of which can impact production schedules, project timelines, and customer satisfaction. The roots of these problems often lie in complex supply chain logistics, poor supplier coordination, and inadequate tracking mechanisms.
Impact on the Supply Chain
The repercussions of delivery issues are far-reaching:
- Production Delays: Late deliveries can halt production lines, leading to downtime and increased costs.
- Project Overruns: Projects may exceed timelines and budgets if essential materials are delayed, affecting overall project delivery and profitability.
- Customer Dissatisfaction: Failure to meet customer expectations due to delayed project completion or product availability can harm business reputation and customer relationships.
- Increased Costs: Expedited shipping to compensate for delays, handling returns of incorrect or damaged goods, and additional administrative work to resolve delivery issues contribute to increased operational costs.
Solutions for Minimizing Disruptions
Addressing delivery issues requires a comprehensive approach that includes better planning, supplier management, and the use of technology:
- Improved Supplier Selection and Management: Careful selection of reliable suppliers and ongoing performance monitoring can reduce the risk of delivery issues. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication are key.
- Advance Planning and Inventory Management: Building buffer stock and implementing effective inventory management practices can mitigate the impact of delivery delays.
- Diversification of Suppliers: Relying on a single supplier for critical components increases vulnerability. Diversifying suppliers across different geographic locations can provide alternatives in case of disruptions.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Coordination and Tracking
Technology plays a pivotal role in improving supplier coordination and delivery tracking, offering solutions to minimize delivery disruptions:
- Supply Chain Management Software: These platforms offer end-to-end visibility of the supply chain, enabling better coordination and management of suppliers, orders, and inventory.
- Real-Time Tracking Systems: GPS and RFID technology can provide real-time tracking of shipments, allowing procurement teams to monitor delivery status and proactively address potential delays.
- Supplier Portals: Online portals can facilitate communication between buyers and suppliers, streamline order processing, and provide updates on order status and shipment tracking.
- Predictive Analytics: Advanced analytics tools can predict potential delivery issues by analyzing historical data and current trends, enabling procurement teams to take preventive actions.
Conclusion
Delivery issues in procurement can severely disrupt the supply chain, but with strategic planning, effective supplier management, and the use of technology, these disruptions can be minimized. Improved coordination and real-time tracking capabilities enable procurement teams to stay ahead of potential problems, ensuring smoother operations and maintaining the integrity of the supply chain. By leveraging technology and adopting best practices in supplier management and inventory planning, organizations can enhance their resilience to delivery challenges, supporting business continuity and customer satisfaction.
10. Choosing the right vendors
The Significance of Vendor Selection
Selecting the right vendors is a critical decision in the procurement process that significantly impacts an organization’s operational efficiency, product quality, and customer satisfaction. The choice of vendors determines not only the cost and quality of inputs but also the reliability of the supply chain and the ability to innovate and respond to market changes. In essence, vendors are not just suppliers; they are strategic partners that contribute to the organization’s competitive advantage and alignment with business values and sustainability goals.
The Vendor Selection Process
The process of selecting vendors involves several key steps designed to ensure that suppliers can meet the organization’s needs in terms of product quality, cost-effectiveness, reliability, and ethical practices. These steps include:
- Requirement Definition: Clearly defining procurement needs, including specifications for products or services, delivery schedules, and quality standards.
- Market Research: Identifying potential vendors through market research, trade fairs, and industry recommendations.
- Request for Proposal (RFP)/Quotation (RFQ): Issuing RFPs or RFQs to shortlisted vendors to gather detailed information on their offerings and capabilities.
- Evaluation and Comparison: Assessing vendor proposals based on criteria such as price, quality, delivery terms, and after-sales service. This may also involve evaluating the vendor’s financial stability, reputation, and compliance with environmental and social standards.
- Negotiation and Selection: Negotiating terms with preferred vendors and making a final selection based on the best fit for the organization’s needs.
Facilitating Vendor Selection with Procurement Software
Procurement software plays a vital role in streamlining the vendor selection process, offering tools and features that facilitate the evaluation and management of vendors:
- Centralized Vendor Information: Procurement software allows for the centralization of vendor information, making it easier to manage vendor profiles, track performance, and access historical data during the selection process.
- Automated RFP/RFQ Management: These platforms can automate the distribution of RFPs and RFQs, collection of responses, and initial screening of proposals, saving time and ensuring consistency in the evaluation process.
- Comparative Analysis Tools: Advanced analytics features enable procurement teams to conduct side-by-side comparisons of vendor proposals based on predefined criteria, helping to identify the best value offerings.
- Supplier Performance Tracking: Procurement software includes tools for monitoring supplier performance over time, providing valuable insights that inform future vendor selection decisions.
- Compliance and Risk Management: These systems can assess vendors against compliance standards and risk factors, ensuring that selected vendors align with corporate values and legal requirements.
Conclusion
Choosing the right vendors is a complex but crucial component of procurement that affects nearly every aspect of an organization’s operations. By employing a structured vendor selection process and leveraging the capabilities of procurement software, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals, values, and operational requirements. The right vendors are key partners in achieving business success, providing the foundation for a strong, reliable supply chain that supports organizational objectives and market responsiveness.
Conclusion
it’s evident that the procurement function encapsulates a complex array of activities, each with its own set of challenges. However, it’s also clear that with every challenge comes an opportunity to innovate, streamline, and enhance the procurement process to better serve organizational goals.
The journey through these challenges underscores the indispensable role of strategic thinking, process optimization, and, critically, the adoption of advanced procurement technologies. From managing risks and enhancing supplier relationships to ensuring compliance and optimizing purchasing processes, the solutions presented aim to empower procurement professionals to turn potential obstacles into stepping stones towards operational excellence.
Key takeaways include the importance of building strong, transparent relationships with suppliers and stakeholders, leveraging data for informed decision-making, and utilizing procurement software to automate and simplify complex processes. Additionally, the emphasis on selecting the right vendors and the strategic management of contracts and deliveries highlights the necessity of a meticulous and proactive approach in modern procurement practices.
As organizations look to the future, the role of digital transformation in procurement cannot be overstated. The integration of cutting-edge procurement software and technologies is not merely a trend but a fundamental shift towards more efficient, transparent, and resilient procurement processes. These tools not only address the immediate challenges but also pave the way for continuous improvement and innovation in procurement strategies.
In conclusion, mastering procurement in today’s fast-paced and ever-changing business environment requires a blend of strategic foresight, operational agility, and technological prowess. By embracing the solutions and best practices outlined in this exploration, businesses can navigate the complexities of procurement with confidence, achieving not only cost efficiencies but also enhancing their value proposition and securing a competitive edge in the market.
As we move forward, let us view the challenges in procurement not as obstacles but as opportunities to drive forward with innovative solutions, strategic partnerships, and a commitment to excellence. The future of procurement is bright for those ready to embrace change, invest in technology, and foster a culture of continuous improvement and strategic collaboration.
Preview AI Intake for Orders
Take the product tour to see how the new intake experience works.